Table 3.
Inhibition of human sEH by amide derivatives substituted with oxyoxalamide function
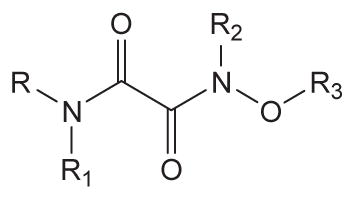
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | R | R1 | R2 | R3 | Human sEH IC50 a (nM) | Solubilityb (μM) |
| 17d |
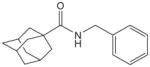
|
>1000 | 40 | |||
| 18 |
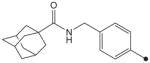
|
H | H | CH3 | 280 | NDc |
| 19 |
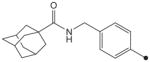
|
H | H |
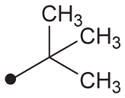
|
408 | ND |
| 20 |
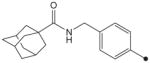
|
H | CH3 | CH3 | 190 | ND |
| 21 |
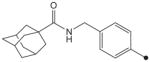
|
CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | 204 | ND |
| 22 |
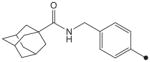
|
H | H |
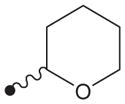
|
>1000 | ND |
| 23 |
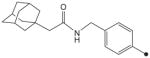
|
H | CH3 | CH3 | 69 | 156 |
| 24 |
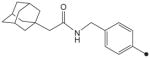
|
CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | 7.9 | 625 |
| 25 |
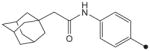
|
H | CH3 | CH3 | 35 | 78 |
| 26 |
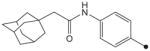
|
CH3 | CH3 | CH3 | 4.4 | 156 |
| 2e |
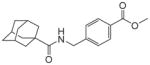
|
9.1 | 125 | |||
| IK950e |
|
14 | 625 | |||
Test compounds prepared in DMSO were reacted with human sEH (1 nM) for 10 min in 25 mM Bis–Tris/HCl buffer (202 μL; pH 7.0) at 30 °C. The fluorescent substrate (CMNPC; [S] = 5 μM) was then introduced to the incubation mixture. Inhibition potency against the human sEH was determined by measuring the appearance of the 6-methoxy-2-naphthaldehyde with an excitation wavelength of 330 nm and an emission wavelength of 465 nm for 10 min on a fluorometer. Results are averages of three separate measurements. See the Supplementary data for the detailed procedures.
Water solubility was determined by adding a variety of concentrations of a test compound prepared in DMSO to 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) in a final ratio of 5:95 (v/v). The turbidity of the water solution was measured at 650 nm to determine solubility in water. Results are the average of triplicate determinations.
Not-determined because the inhibition results were not potent enough compared to that of other derivatives.
Amide inhibitor with no substitution by oxyoxalamide function.
