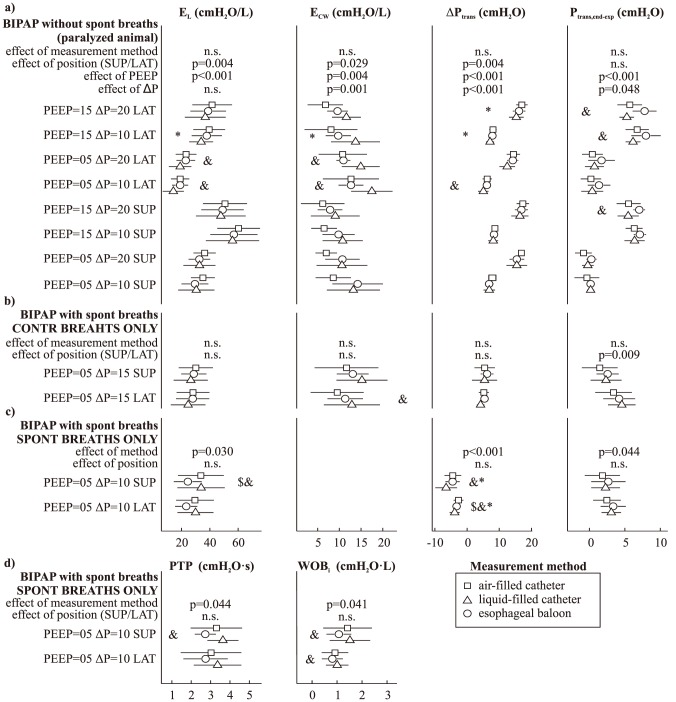
Figure 4. Average value (±SD) of the parameters derived from esophageal pressure measurements under different settings of BIPAP (biphasic positive airway pressure) mechanical ventilation: a) controlled ventilation (with animal paralyzed using atracurium bromide); b) assisted ventilation (allowing unsupported spontaneous breaths), considering only the controlled breaths; c) and d) assisted ventilation, considering only the unsupported spontaneous breaths.
PEEP: positive end-expiratory pressure (cmH2O); ΔP: driving pressure (cmH2O); SUP, LAT: supine or right lateral decubitus; EL, Ecw: lung and chest wall elastance; ΔPtrans: inspiratory change in transpulmonary pressure; Ptrans,end-exp: end-expiratory value of transpulmonary pressure; PTP: pressure-time product; WOBi: inspiratory work of breathing. The p-value of the effect of measurement method, position (SUP/LAT), PEEP and ΔP was computed using a general linear model approach (n.s. corresponds to p-value>0.05). &: significant (p<0.05) difference between indexes estimated using the air-filled and liquid-filled catheter, using a paired t-test. Similar notation for the comparisons of the balloon catheter with the air-filled ($) and liquid-filled (*) catheter.