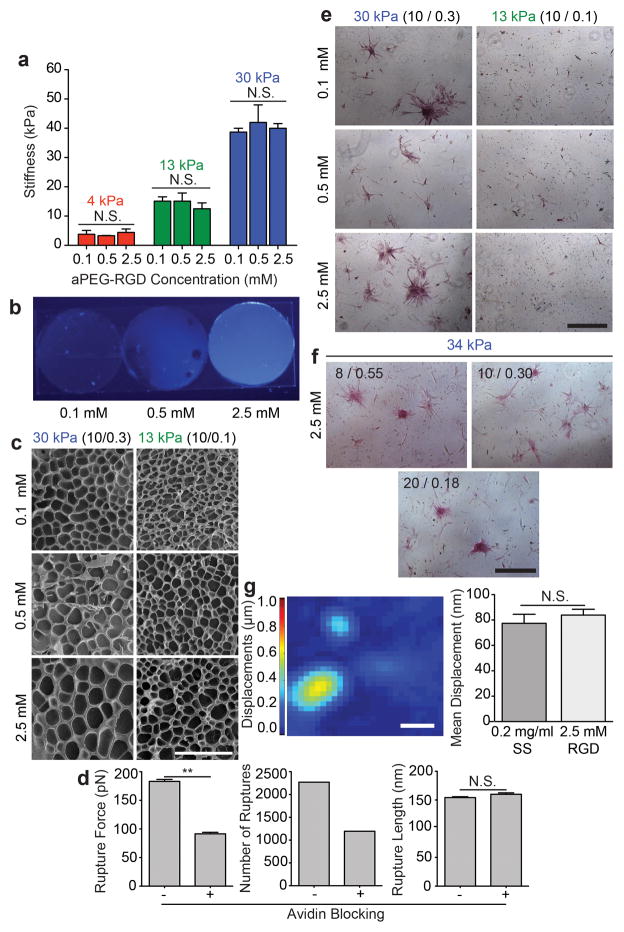
Fig 3. Direct incorporation of a short adhesive peptide to the PA substrate.
a, Elastic modulus measured via AFM (n = 3; N.S. = not significant). b, aPEG-RGD-dye incorporation is detected under UV light. c, SEM images of PA hydrogels of indicated stiffness made with varying RGD concentration (scale bar, 50 μm). d, Measured rupture force (left), number of events (middle), and rupture length (right) for rupture events that occurred on 10/0.3 30 kPa hydrogels coated with PEG-biotin (n = 1000; mean ± S.E.M.; N. S. = not significant; **p<0.0001). e, ALP staining of ASCs on 13 kPa and 30 kPa hydrogels with low, medium, and high concentrations of RGD (scale bar, 500 μm). f, ALP staining of ASCs on 30 kPa hydrogels of varying monomer to crosslinker ratio and constant high concentration of RGD after 14 days of culture in normal media (scale bar, 500 μm). g, Representative displacement map (left) of embedded fluorescent particles resulting from ASC traction forces on a 30 kPa hydrogel with 2.5 mM RGD. Mean displacement is shown (right) for a collagen coated hydrogel (0.2 mg/ml sulfo-SANPAH and 50 μg/mL collagen I) and a PA-PEG-RGD hydrogel (2.5 mM RGD). (n = 30; mean ± S.E.M; N.S. = not significant; scale bar, 50 μm).