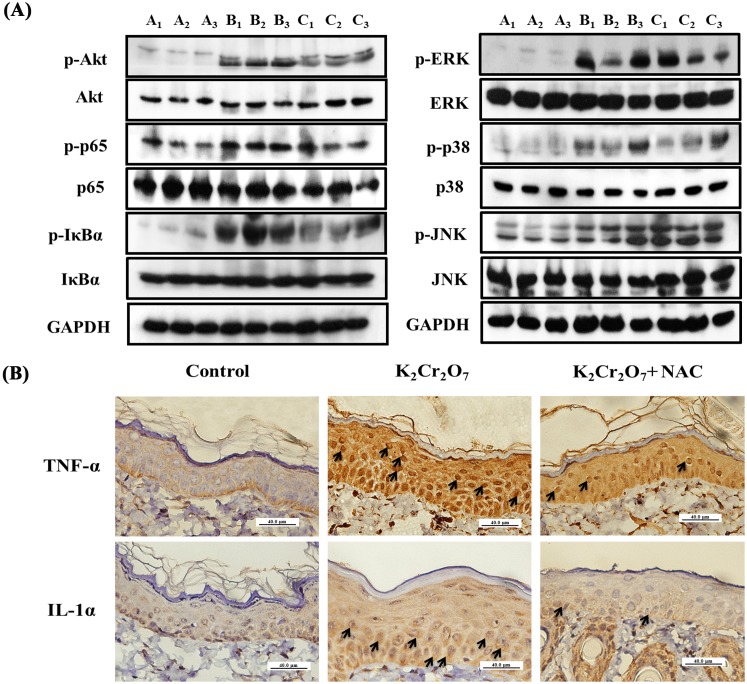
Figure 7. NAC administration decreased the activation of the Akt, NF-κB, MAPK pathway and expression of cytokines in albino guinea pig.
Three groups of GP (A, B, and C; n = 3 per group) were used. Group A and Group B were fed only ordinary food, while Group C was fed ordinary food and 1200 mg/kg/day of NAC. Group A were injected with 0.2 ml of saline solution (control group) and Group B and Group C were injected with 2 mg/ml Cr(VI) in saline (Cr(VI) exposed Group). Forty-eight hours after these injections, skin specimens were taken for analysis. (A) Epidermal protein was extracted for western blot analysis and results demonstrated the activation of phospho-Akt, phospho-p65, phospho-IκBα, phospho-ERK, phospho-p38 and phospho-JNK in Group B, but the phosphorylation of these proteins were inhibited by NAC administration. A1, A2 and A3 reflect the three independent specimens from the control group. B1, B2 and B3 reflect the three independent specimens from the Cr(VI) exposed group. C1, C2 and C3 reflect the three independent specimens from the Cr(VI)+NAC exposed group. (B) Skin biopsy from the control group showed no staining of TNF-α and IL-1α in the epidermis (400×). The Cr(VI) exposed group induced the expression of TNF-α (arrow) and IL-1α (arrow) (400×). However, the Cr(VI)+NAC exposed group showed significant reduction in TNF-α and IL-1α in the epidermis (400×). Scale bars: 40 µm.