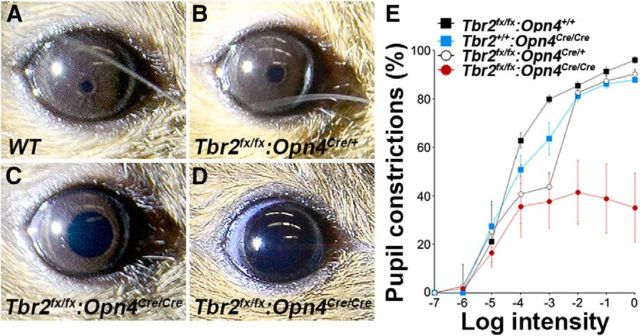
Figure 7.
Tbr2 is required for normal PLR. A–D, Representative PLR images of WT control (A), Tbr2flox/flox:Opn4Cre/+ (B), and Tbr2flox/flox:Opn4Cre/Cre (C, D) pupils in response to a 30 s bright light stimulation (0 log Io). Some Tbr2flox/flox:Opn4Cre/Cre mice (3 of 5) showed an ∼60% pupil constriction (C), and others (2 of 5) were unable to maintain pupil constriction (D). E, Quantification of the PLR as a function of light intensity. Data were collected from five animals of each genotype. A two-way ANOVA revealed significant light intensity (F(7,119) = 58.74, p < 0.001), phenotype (F(2,119) = 29.64, p < 0.001), and light intensity × phenotype (F(14,119) = 4.75, p < 0.001) effects. The maximum constriction was 96.03 ± 1.36% in the WT control mice, 90.22 ± 1.94% in the Tbr2flox/flox:Opn4Cre/+ mice, 38.35 ± 5.41% in the Tbr2flox/flox:Opn4Cre/Cre mice, and 87.85 ± 0.89% in Opn4Cre/Cre mice. Io = 15 mW·cm−2 white light. Error bars represent SEM.