Figure 2.
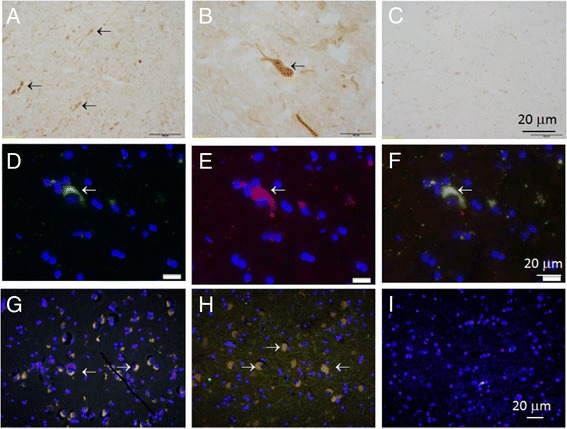
Colocalization of α-syn with oxi-γ-syn in amygdala and substantia nigra in AD with LB patients. Frozen (two top rows) and paraffin-embedded sections (bottom row) of substantia nigra and amygdala of healthy (A, G) and AD patients with DLB (H, I). The top row: frozen sections (A and B) were stained using H&R- DAB –procedure and oxi-γ-syn antibody. A- substantia nigra from K46 healthy individual, B - substantia nigra from S3 patient (AD with LB), C- the same as in A, but without primary antibody. In the middle row the sections of substantia nigra from S3 patient were stained by oxi-γ-syn antibody; D - α-syn antibody (Abcam ab6162, antisheep); E - oxi-γ-syn antibody; F - colocalization of both antibodies. The bottom row. The sections were double stained with antibody against α-syn (red, Abcam ab 6162, antisheep) and oxi-γ-syn (green, antirabbit, homemade antibody). Yellow cytoplasmic staining is shown by an arrow in a sample from amygdala of K21-healthy donor (G) and in a sample from amygdala taken from a patient S4 with AD with LB (H) substantia nigra from patient S3 suffering from mild AD with LB (I). Antibody to unmodified γ-syn (clone 1H10D2, Antagene) (red) reveals a weak staining of unmodified γ-syn in the cytoplasm of neurons.
