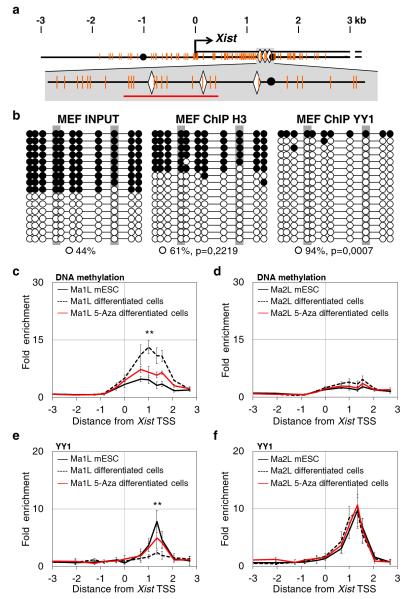
Figure 2. Allelic binding of YY1 in differentiating cells is DNA-methylation dependent.
(a) Top: map of the 5′ proximal Xist region as in Fig. 1, with CpG dinucleotides indicated by orange vertical bars. Bottom: enlargement of the region encompassing the YY1 binding sites (b) Bisulfite sequencing of input and DNA immunoprecipitated using the histone H3 and YY1 antibody in primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF). Open circles and black circles represent unmethylated and methylated CpG, respectively. P-values are calculated using Fisher test comparing IP and input data. (c) MeDIP analysis of DNA methylation across the Xist promoter region in Ma1L and Ma2L mESC (black line), and in untreated (dotted line) and 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine treated (5-Aza, red line) differentiating cells. Primers amplifying regions devoid of CpG dinucleotides were used for calculating the background enrichment levels. Values are represented as fold enrichment relative to background. Three independent MeDIP experiments were performed. (d) ChIP analysis of YY1 binding in Ma1L and Ma2L mESC, and in untreated and 5-Aza treated differentiating cells. Statistical evaluation of differences between untreated and 5-aza treated differentiated cells is provided for the position displaying the highest enrichment; *** p<0.001; ** p< 0.01; * p<0.05 (Student’s t-test). Error bars represent SD, n=5.