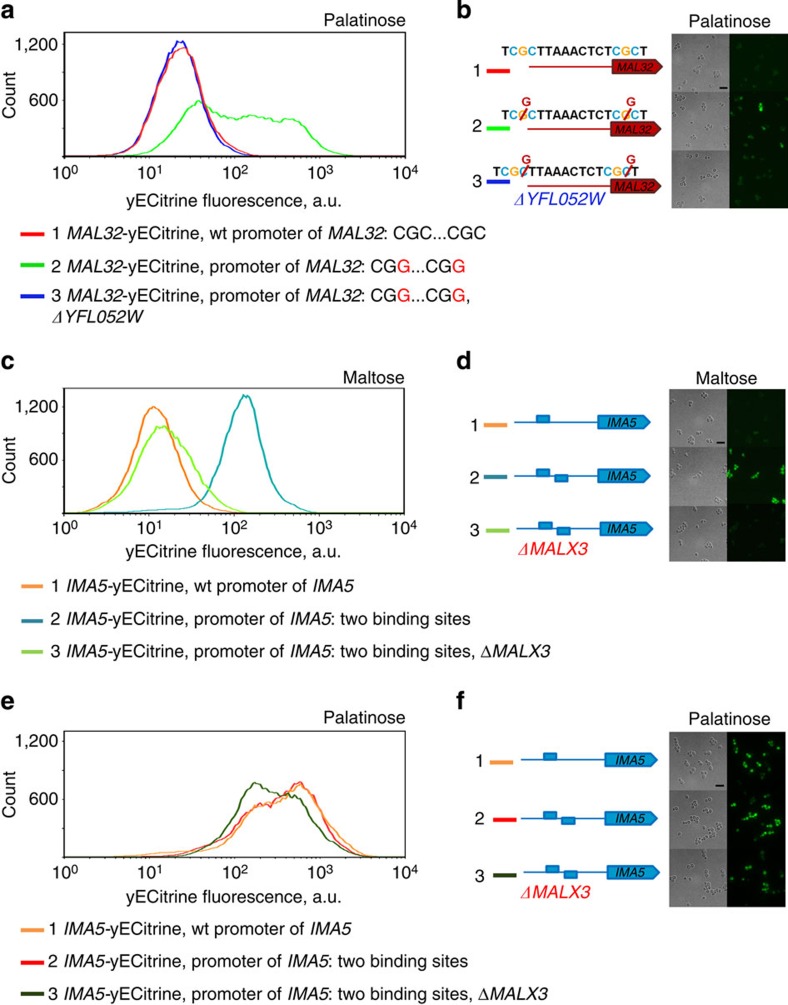
Figure 4. Yfl052w and Malx3 regulators show different DNA-binding specificity.
(a) Two point mutations in a maltose-inducible promoter yield a palatinose-inducible promoter. (1) Histogram of the fluorescence signal of a strain with a yECitrine-tagged MAL32 gene. This maltose-specific reporter gene shows no expression in palatinose and can be used to estimate the background fluorescence levels. (2) Single nucleotide C to G substitution in both CGC motifs in the upstream Malx3 binding site of the of MAL32 promoter leads to expression of this gene in palatinose. (3) Deletion of palatinose-specific regulator Yfl052w abolishes the expression of the mutant promoter. (b) Fluorescence microscopy images of the same strains reported in a. (c) Increasing the number of CGG-containing binding sites in a palatinose-inducible promoter yields a promoter that is responsive to maltose. (d) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of the strains shown in c in maltose. (e) Increasing the number of CGG-containing binding sites does not affect the expression of the palatinose-inducible gene IMA5 in palatinose. (f) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of the strains shown in c in palatinose. Scale bar is included in the upper left image of b,d,f and equals 10 μm. Each experiment was repeated at least three times with two biological replicates.