Figure 5.
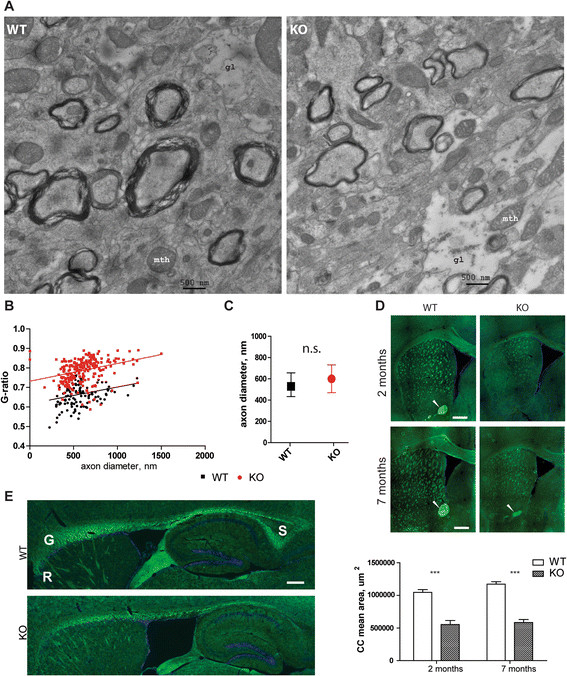
Myelination is impaired in Mcoln1 −/− mice. (A). Representative electron micrographs of CA1 stratum radiatum in 7 month-old control (WT) and Mcoln1 −/− (KO) mice showing reduced thickness of myelin sheaths. (B). G-ratio (axon diameter/fiber diameter) plotted against axon diameter shows reduced degree of myelination in Mcoln1 −/− (124 axons; 4 mice) compared to wild-type (231 axon; 4 mice) 7 month-old littermates, p (clustered rank-sum test) = 0.018. (C). Comparison of axon diameters revealed no significant difference between control (WT) and Mcoln1 −/− (KO) littermates. Data presented as median values with interquartile range, n.s., p (clustered rank-sum test) = 0.28. (D). Representative images of FluoroMyelin Green- stained coronal sections show reduced myelination of corpus callosum, internal capsule and anterior commissure (indicated by white arrowheads) in Mcoln1 −/− brain and thinning of the corpus callosum (n = 3 per genotype at 2 months, n = 5 per genotype at 7 months; p (t-test) <0.01). (E). Representative images of FluoroMyelin Green- stained sagittal sections (counterstained with DAPI) demonstrate malformation of the corpus callosum in the Mcoln1 −/− at 2 months. S-splenium, G-genu, R-rostrum. Scale bars = 0.5 mm.
