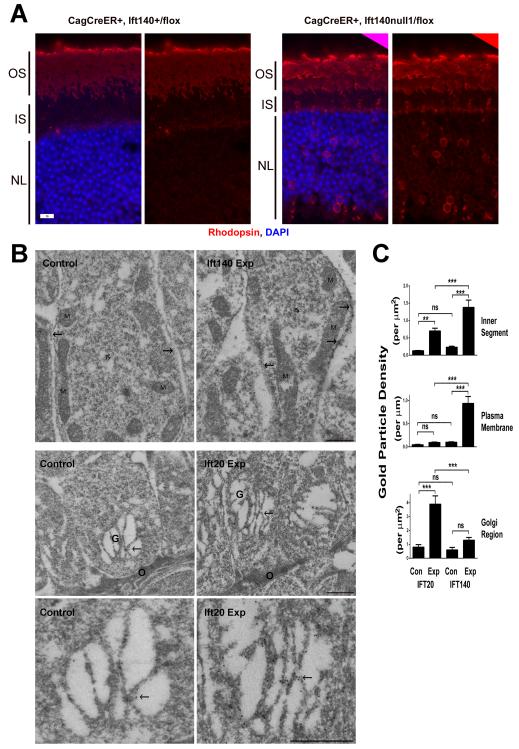
Figure 3. Acute deletion of Ift140 causes opsin accumulation in the plasma membrane.
A. Paraffin section of control and experimental retinas harvested 48 hr after administration of tamoxifen. Note the accumulation of rhodopsin (red) in the inner segment (IS) and around the nuclei (blue, NL) in the experimental animals. OS, outer segment. Scale bar is 10 μm.
B. Immunogold labeling of rhodopsin of Ift140 (top row) and Ift20 (middle and bottom row) control and experimental retinas harvested 48 hr after administration of tamoxifen. Arrows indicate plasma membrane in the upper row and the Golgi complex (G) in the middle and bottom row. The upper row shows sections through the distal region of the inner segment (IS); M, mitochondria. The middle row shows sections through the proximal region of the inner segment; the outer limiting membrane (O) represents the proximal limit of the inner segment and consists of adherens junctions between adjacent photoreceptor cells and Mueller cells. The lower row are higher magnification micrographs of the Golgi complexes shown in the middle row. Scale bars are 500 nm.
C. Quantification of gold particles. Units are per micron squared for the inner segment and Golgi region and per micron for the plasma membrane. ns, not significant; *p=0.01-0.05; **p=0.001-0.01;***p<0.001.