FIG 4 .
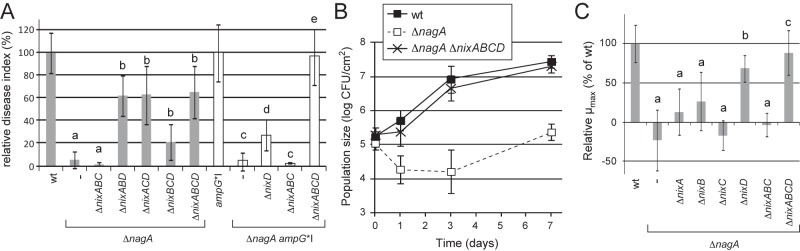
Nix TonB-dependent transporters of X. campestris pv. campestris are epistatic to the nagA phenotype during plant infection and growth in cabbage xylem sap. (A and B) X. campestris pv. campestris strains (OD600 = 0.05) were inoculated onto leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana Sf-2 ecotype by piercing. (A) Disease index scored at 8 days postinoculation (dpi), presented as percentages of the value for the wt strain (gray) or the ampG*I strain (white). Standard deviations were obtained from at least 16 leaves from 4 plants. Values significantly different (P value <0.0001) from those for the wt strain (a; sensitivity), both the wt and ΔnagA strains (b; partial epistasis), the ampG*I strain (c; sensitivity), the ΔnagA ampG*I and ampG*I strains (d; partial epistasis), and the ΔnagA ampG*I strain (e; total epistasis) are indicated. (B) IGC in the inoculated area. Bacteria were extracted from infected leaves at different dpi and counted by plating serial dilutions. Standard deviations were obtained from at least 3 independent samples. (C) Epistasis on the ΔnagA mutant during growth in xylem sap from Brassica oleracea cv. Bartolo F1 cabbages (OD600 = 0.01 at time zero). At different time points, CFU were counted by plating serial dilutions. Maximal specific growth rates (µmax) were calculated between 3 and 9 h of growth from CFU counts. Standard deviations were obtained from at least three independent experiments. Values significantly different (P < 0.0001) from those for the wt strain (a; sensitivity), both the wt and ΔnagA strains (b; partial epistasis), and the ΔnagA strain (c; total epistasis) are indicated.
