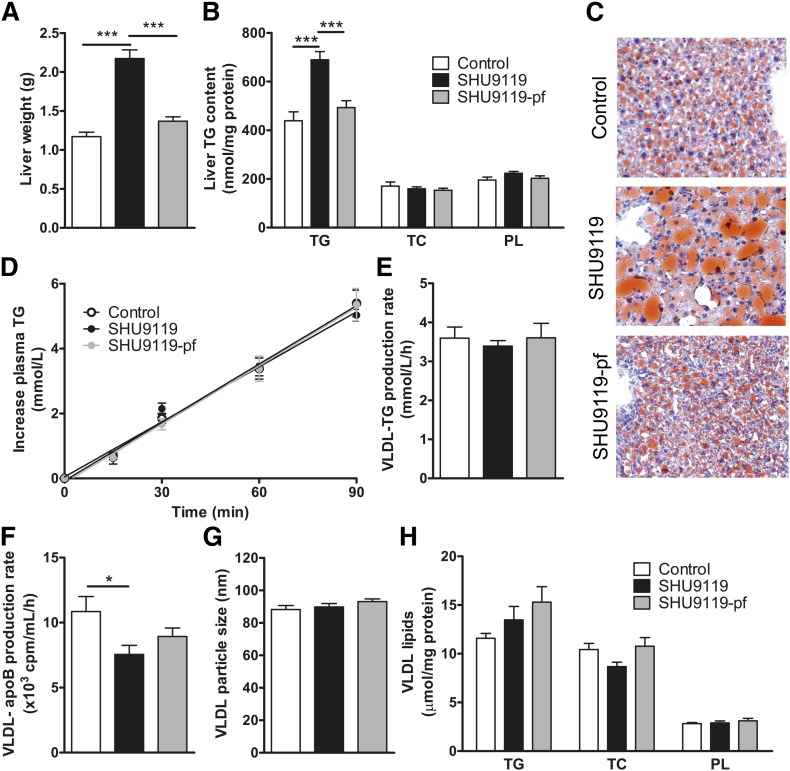
Fig. 3.
SHU9119 induces hepatomegaly and steatosis only in ad libitum-fed mice. APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice were treated intracerebroventricularly with vehicle (n = 21) or SHU9119 (5 nmol/day) while being fed ad libitum (n = 21) or being pair-fed (pf) to the vehicle-treated group (n = 20). After 17 days of treatment, some of the mice were euthanized (n = 10–11 per group) to collect organs and determine liver weight (A), and to determine liver content of TGs, TC, and PLs (B). Frozen liver samples were sectioned and stained with a neutral lipid staining (Oil Red O) and hematoxylin, and representative pictures are shown (C). The remaining mice (n = 8–10 per group) were fasted 4 h, and consecutively injected with Tran35S label and tyloxapol, and blood samples were drawn up to 90 min after tyloxapol injection. Plasma TG concentration was determined and plotted as the increase in plasma TG relative to t = 0 (D). The rate of TG production was calculated from the slopes of the curves from the individual mice (E). After 120 min, the total VLDL fraction was isolated by ultracentrifugation, and the rate of newly synthesized VLDL-apoB was determined (F). The VLDL fractions were assayed for particle size (G) and lipid content (H). Values are means ± SEM. * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001 compared with control.