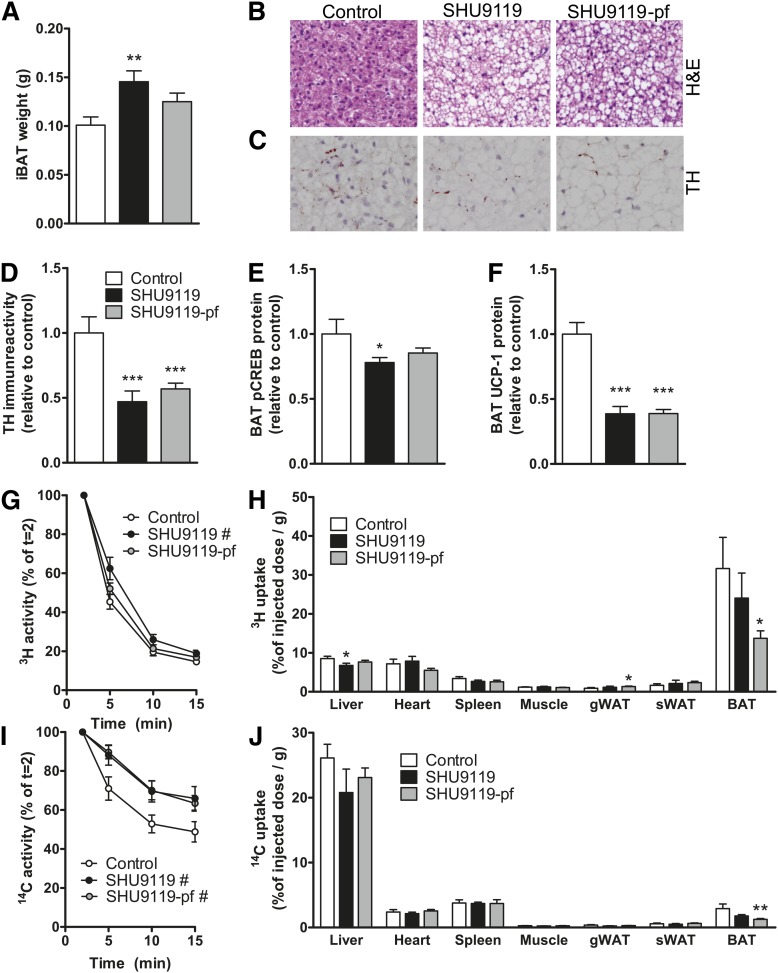
Fig. 4.
SHU9119 causes malfunction of BAT. APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice were treated intracerebroventricularly with vehicle (n = 21) or SHU9119 (5 nmol/day) while being fed ad libitum (n = 21) or being pair-fed (pf) to the vehicle-treated group (n = 22). After 17 days of treatment, some of the mice were euthanized (n = 10–11 per group), and iBAT was quantitatively removed. iBAT was examined for weight (A), morphology, as assessed by H&E staining (B), and TH content (C, D). In iBAT, protein content of p-CREB (E) and UCP-1 (F) were determined. In a second experiment, after 14 days of icv treatment with vehicle (n = 8) or SHU9119 (5 nmol/day) while being fed ad libitum (n = 5) or being pf to the vehicle-treated group (n = 9), mice were fasted 4 h and consecutively injected with [3H]TO- and [14C]CO-labeled VLDL-like emulsion particles. Plasma [3H]TO (G) and [14C]CO (H) were determined at the indicated time points and plotted relative to the dosage at t = 2 min. At 15 min after injection, organs were isolated, and uptake of the 3H-activity (H) and 14C-activity (J) was determined. Values are means ± SEM. # P < 0.05, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 compared with control.