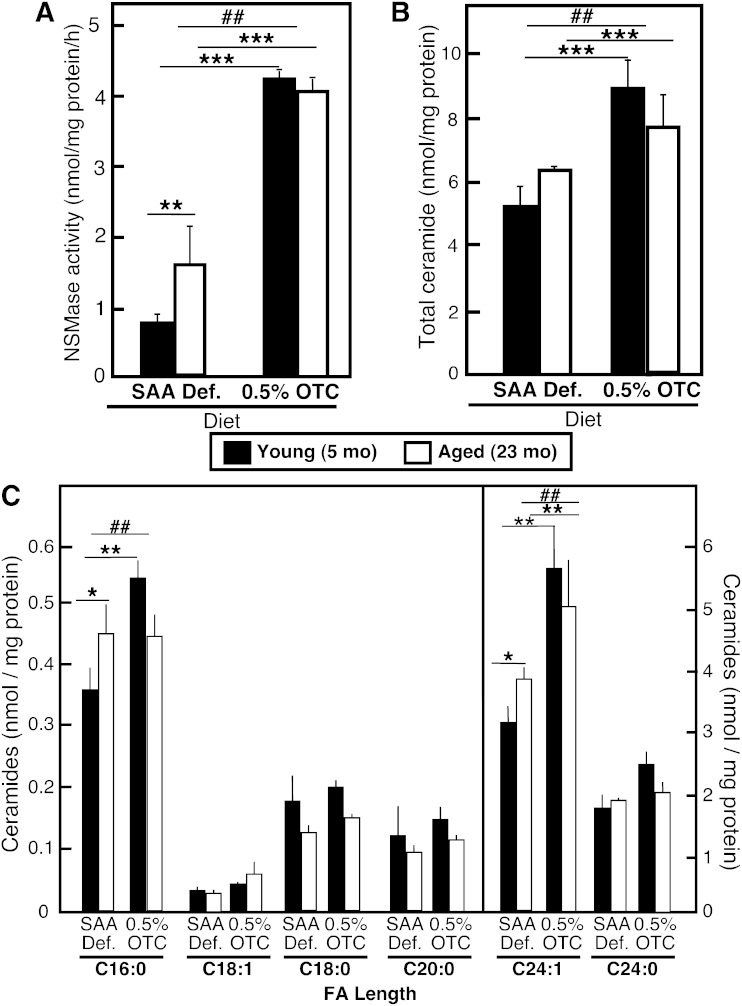
Fig. 3.
Effect of dietary OTC supplementation on nSMase activity and ceramide levels in mouse livers. Young and aged C57Bl6 mice were placed on either a 0.5% OTC or a SAA def. control diet for 4 weeks. nSMase activity (A) was assessed in whole liver homogenates (40 μg of protein/assay) using a fluorescently labeled NBD-SM as a substrate. Total ceramide (B) and ceramide species with different FA length (C) were measured in total lipid extracts by HPLC-ESI/tandem mass spectrometry. Mean values ± SD are shown (n = 3–4 mice in each group). Statistical analysis was done by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest analyses. The statistical significance of the main effects (aging and diet) are shown with asterisks (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). The statistical significance of the interaction effect is shown with number signs (##P < 0.001).