Fig. 6.
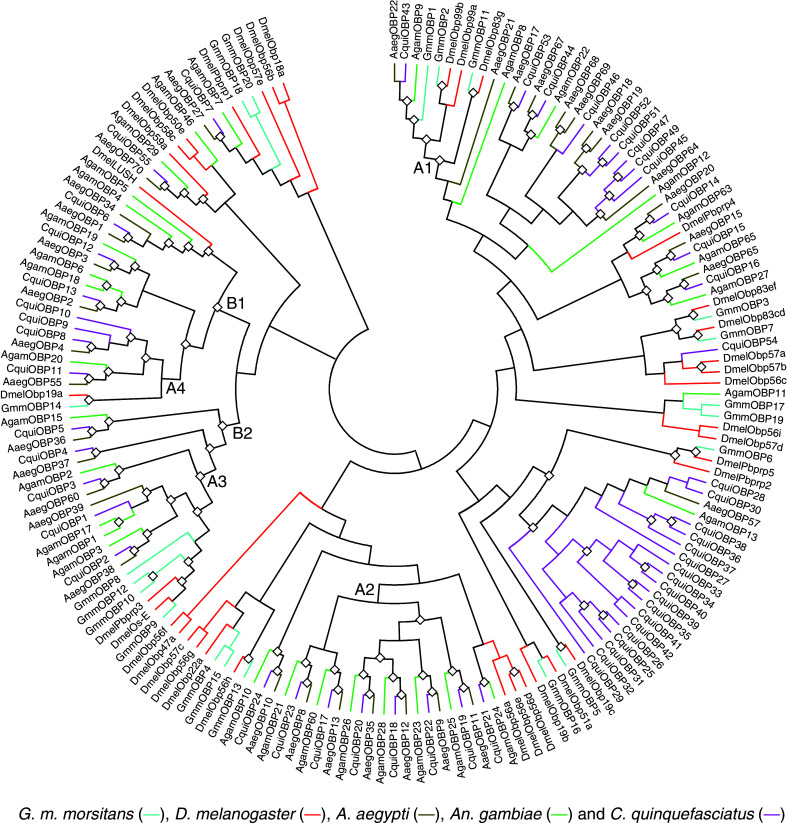
Phylogenetic tree (topology only) of OBPs in Diptera including Glossina morsitans morsitans (Gmm in turquoise), Drosophila melanogaster (Dmel in red), Aedes aegypti (Aaeg in dark yellow), Anopheles gambiae (Agam in green) and Culex quinquefasciatus (Cqui in pink). Diamonds indicate the nodes with 70% bootstrap support. Proteins labelled with squares are dimer OBPs. The clades labelled with A1, A2, A3 and A4 reflect the correlation between the phylogenetic relationships of the OBPs and the evolution of the species of Diptera based on classic taxonomy (Fig. 7). There are two main orthologous groups (B1 and B2) with strong boostrapping support and showing a clear phylogenetic relationship amongst the OBPs from the different species
