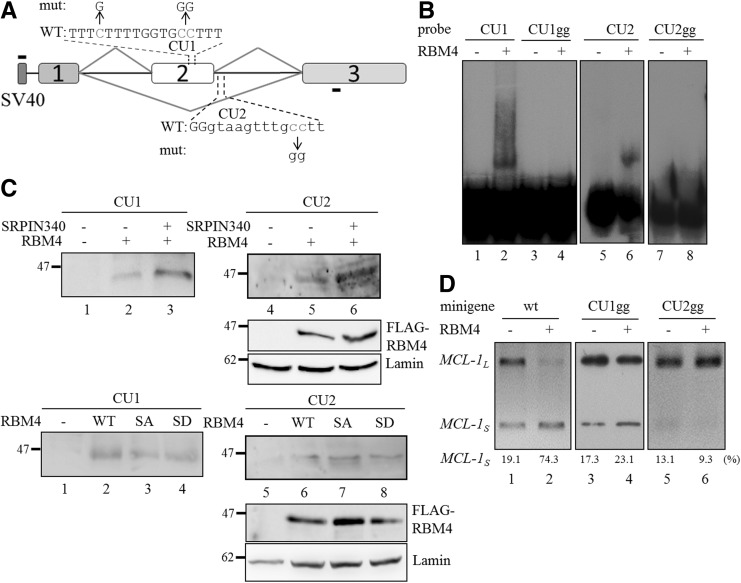
FIGURE 5.
RBM4 mediates the exclusion of MCL-1 exon 2 by binding directly to the exonic and intronic CU-rich elements. (A) The diagram presents the sequence of the exonic and downstream intronic CU-rich elements of MCL-1 exon 2. The mutant reporters contained cytosine-to-guanine nucleotide substitutions in the CU1 and CU2 elements. (B) The mock eluate from Ni2+-nitrilotriacetic acid-agarose resin or 1 µg of recombinant His-tagged RBM4 protein was incubated with 10 nM DIG-labeled probes. The mixtures were fractionated in 8% native acrylamide gel and transferred to the nylon membrane. The membrane was probed using an HRP-conjugated anti-DIG Fab fragment. (C) MCF-7 cells were mock-transfected or transfected with the FLAG-RBM4 expression plasmid, followed by vehicle or SRPIN340 treatment. The nuclear extracts prepared from the various transfected cells were incubated with the DIG-labeled CU1 and CU2 probes, followed by UV crosslinking. The reactions were analyzed using an immunoblotting assay with the anti-FLAG M2 antibody. (D) The wild-type MCL-1 minigene and the derived mutants (CU1gg and CU2gg) were cotransfected with the empty vector or FLAG-RBM4 expression vector into MCF-7 cells. The PCR product of spliced transcript of each minigene was analyzed using electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel.