Fig. 4.
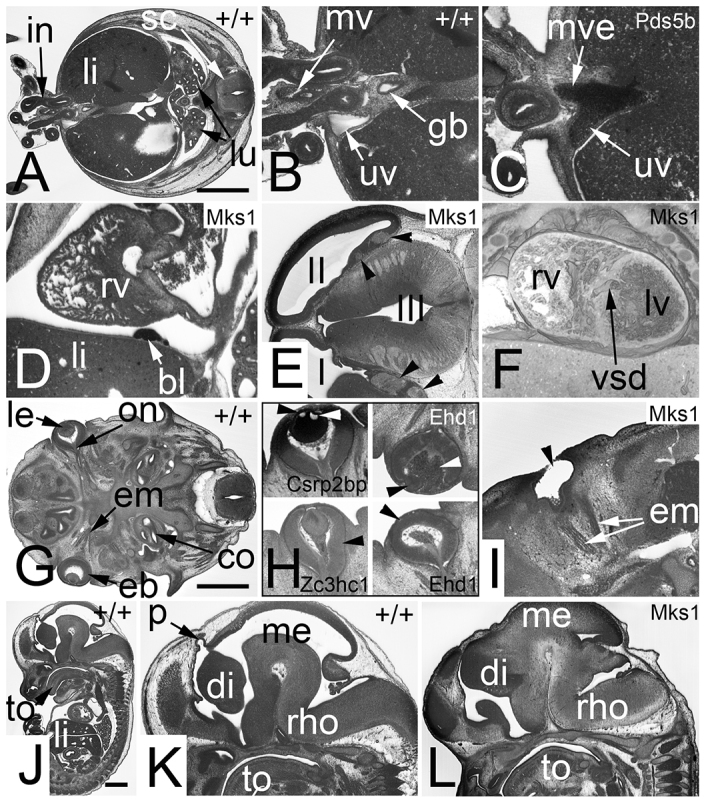
Severe and dangerous defects (Sc2, Sc3). Potential pre- or perinatal life-threatening defects (Sc2 in A–F). Abnormalities that reduce life span (Sc3 in G–L). (A) Axial section through a wild-type (+/+) embryo. Note the intestine (in) forming the umbilical hernia and the liver (li). (B) Zoom into the junction of umbilical hernia and body. Note the umbilical vein (uv) right to the intestine and the mesenterial vessels (mv) between the intestinal segments leaving and entering the body. (C) A Pds5b−/− embryo in which the vitelline vein (mve) connects with the umbilical vein. (D) Hemangioma-like lesion (bl) in the pericardium of an Mks1−/− embryo. Sagittal resection. (E) Fibroma (arrowheads) in the telencephalon of an Mks1−/− embryo. Axial section. (F) Muscular ventricular septal defect (vsd) in an Mks1−/− embryo. Coronally sectioned 3D model. (G) Axial section through a wild-type embryo. Note the form and position of the eyeball (eb), lens (le), optic nerve (on) and eye muscles (em). (H) Various eye defects are indicated with arrowheads. Vacuolated lens at top (Csrp2bp−/−) left. Displaced lens (black arrowhead) and retro-lental bleeding (white arrowhead) are visible at the top right (Ehd1−/−). A malformed eye ball (abnormal optic cup) is shown at the bottom left (Zc3hc1−/−). An absent lens (vesicle) is marked at the bottom right (Ehd1−/−). (I) A missing eye ball (anophthalmia) in an Mks1−/− embryo. Note that the eye muscles do exist. (J) Sagittal resection through a wild-type embryo. (K) Zoom in of the head region of embryo displayed in J. Note the pineal gland vesicle (p). (l) Missing pineal gland vesicle in an Mks1−/− embryo. Note that also the rest of the diencephalon (di) is malformed. co, cochlea; gb, gall bladder; I, first brain ventricle; II, second brain ventricle; III, third brain ventricle; in, intestine; lu, lung; lv, left cardiac ventricle; me, mesencephalon; rho, rhombencephalon; rv, right cardiac ventricle; sc, spinal chord; to, tongue. Scale bars: 1 mm.
