Fig. 6.
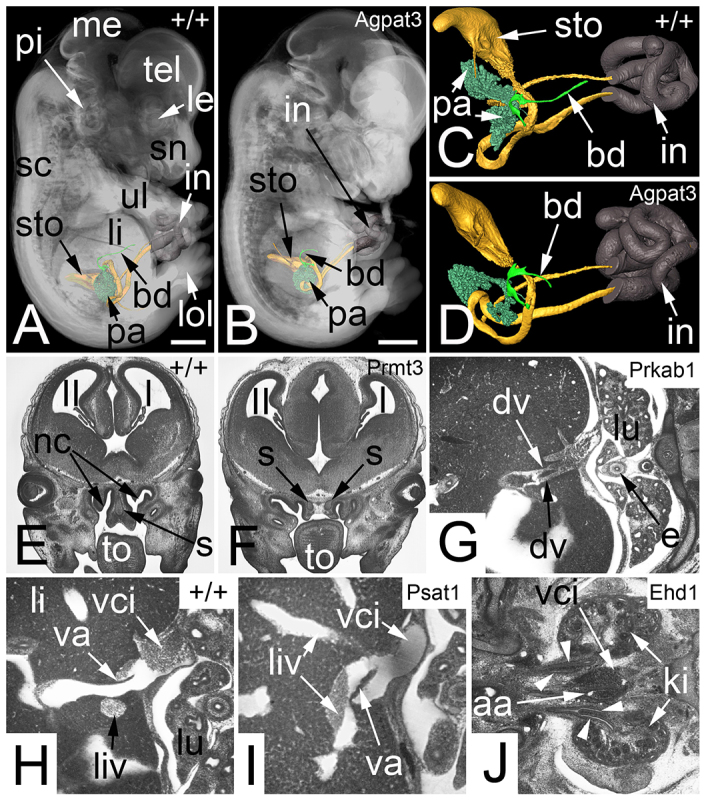
Abnormalities that are not obvious indicators for severe defects (Sc5). (A) Transparent volume rendered 3D model of a wild-type (+/+) embryo combined with surface rendered 3D models of the stomach (sto), pancreas (pa), cystic duct (bd) and intestine (in). (B) Agpat3−/− embryo of the same developmental stage and displayed in the same modality as A. Note the shortness of the cystic duct. (C) Zoom in of A. The cavity of the stomach and the lumen of the intestine (in) are yellow, the wall of the intestine is dark brown and indicates the umbilical hernia. (D) Zoom in of B. (E) Coronal resection through the head of a wild-type embryo. Note the tongue (to) and the nasal septum (s) between the nasal cavities (nc). (F) Prmt3−/− embryo with two nasal septa and a connective tissue space in between. (G) Dual ductus venosus (dv) in an axial section of a Prkab1−/− embryo. (H) Axial section through a wild-type embryo. Note the position of the valve of the ductus venosus (va). (I) Axial section through a Psat1−/− embryo. Note the abnormal position of the valve of the ductus venosus at the connection with a left-sided liver vein (liv). (J) Abnormal ureters in an Ehd1−/− embryo. Note two ureters on the right side and a bifid ureter on the left side (arrowheads). aa, abdominal aorta; dv, ductus venosus; e, esophagus; I, first ventricle; II, second ventricle; ki, kidney; le, lens; li, liver; lol, lower limb; lu, lung; me, mesencephalon; pi, pinna; sc, spinal chord; sn, snout; tel, telencephalon; ul, upper limb; va, valve of ductus venosus; vci, vena cava inferior. Scale bars: 1 mm.
