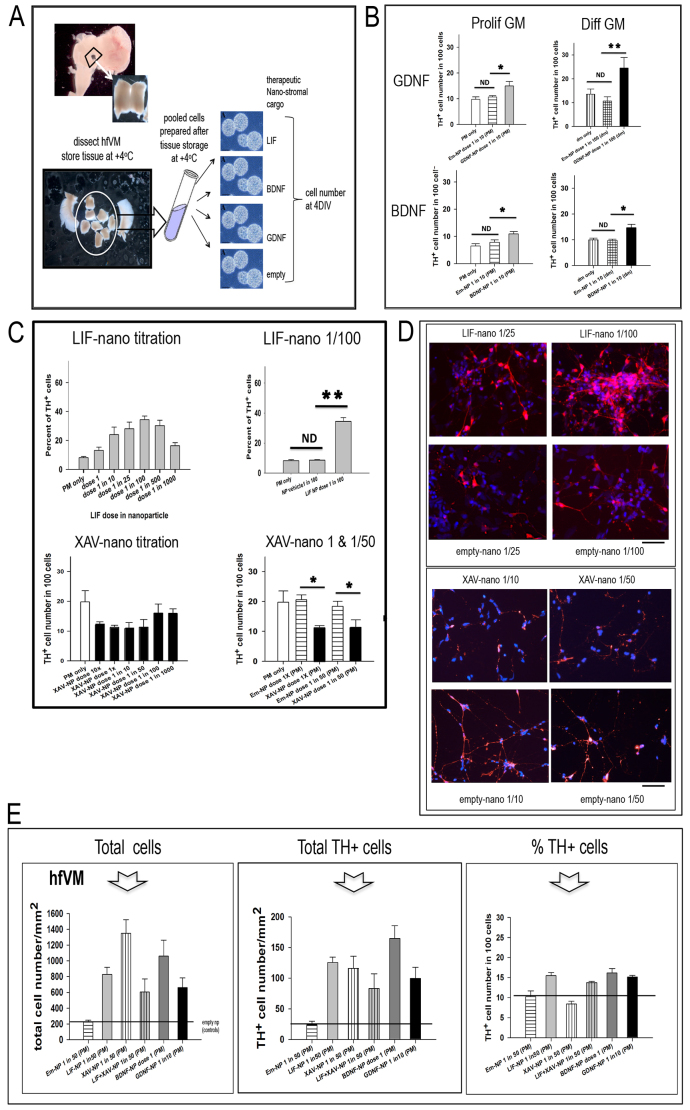
Fig. 4.
Nano-stromal-mediated pro-survival effects might be uncoupled from pro-differentiation effects. (A) Illustrates the procedure for setting up human fetal ventral mesencephalon (hfVM) cultures: the nano-stroma are exemplified for LIF, BDNF and GDNF, with empty-nano as control. hfVM material was obtained at the time of routine termination of pregnancy: fetal age was determined based on crown/rump length. Following dissection, the hfVM was stored at +4°C in HibE for up to 4 days prior to dissociating the cells and coating with nano-stroma. Being of primary human source, no truly identical biological replicates between experiments was possible, but repeat experiments using material from different donors gave similar results for each of the treatments used. Within each experiment there were five replicates per treatment condition. When different treatments were directly compared – as in E – a single batch of donated tissue was used: in some cases cells from multiple donors were pooled prior to aliquoting for treatment to ensure direct comparability. Data are presented as percentage of TH+ cells in the total BIII-tubulin+ cell population. (B) Histograms showing the percentage of TH+ cells in hfVM cultures comparing treatment in either proliferation or differentiation medium (PM or DM, respectively), with or without GDNF-nano (top panels) or BDNF-nano (bottom panels). The experiments shown used either 48-day or 49-day hfVM tissue stored overnight in HibE at +4°C: this was then dissociated into single cells, incubated at 37°C for 16 hours with the various nanoparticle treatments in either PM or DM. The cells were then cultured in DM for 4 days prior to fixing and staining for TH (DA cells) and βIII tubulin (neurons). Both GDNF-nano and BDNF-nano treatment increased the percentage of TH+ cells in the culture when compared with empty-nano controls at equivalent dilution, regardless of treatment in either PM or DM. GDNF-nano/PM one-way ANOVA, F2,11=5.479, P=0.028; GDNF-nano/DM one-way ANOVA, F2,10=5.599, P=0.030; BDNF-nano/PM GDNF-nano/PM one-way ANOVA, F2,11=7.261, P=0.013; GDNF-nano/DM one-way ANOVA, F2,11=9.862, P=0.005. EmNP, empty-nano; ND, no difference; *P<0.05; **P<0.01. (C) Histograms showing the dose response curve based on the percentage of TH+ cells in hfVM cell cultures treated with LIF-nano ranging from 1:1 to 1:1000 in PM for 14 hours prior to growth in DM for 4 days (top left). The donor age was 50 days and the VM cells were prepared freshly prior to treatment. Top right compares the LIF-nano dose that had maximum effect (1:100), resulting in a significantly increased percentage of TH+ cells compared with untreated controls, or cells treated with empty-nano at equivalent dilution. The lower left histogram shows that treatment with XAV-nano decreased the percentage of TH+ cells: in this experiment, the decrease was not significant (P=0.060: lower right histogram). The donor age was 42 days and the tissue had been stored overnight in HibE prior to cell preparation and treatment in PM for 18 hours, then culture in DM 4 days. *P<0.05; **P<0.01. (D) Images of the hfVM experiment described in C, comparing the effects of LIF-nano versus empty-nano at equivalent dilution (left panel) and XAV-nano versus empty-nano at equivalent dilution (right panel). Scale bars: 200 μm. (E) Histograms showing total numbers of βIII-tubulin+ neurons (left panel), and total TH+ cells (centre panel), after the culturing of hfVM cells treated with Thy-1-targeted: LIF-nano; XAV-nano; LIF-nano combined with XAV-nano; BDNF-nano; or -GDNF-nano. The number of TH+ cells, as a percentage of the total number of βIII-tubulin+ neurons is shown in the right hand panel. n=4 in each treatment group where cell counts were taken from five random areas of 1 mm2 per coverslip. Error bars show s.e.m.; pairwise multiple comparison procedures post hoc (Holm-Sidak method). Arrow points to the column for XAV-nano-treated cells, where total cell numbers were increased sixfold (left panel), whereas the percentage of TH+ cells was decreased (right panel): the overall total number of TH+ cells compared with empty-nano controls was fourfold in the presence of XAV-nano. Combined treatment with both LIF-nano and XAV-nano (fourth column) reduced the selective effect of XAV-nano monotherapy on total cell number, and on % TH+ cells.