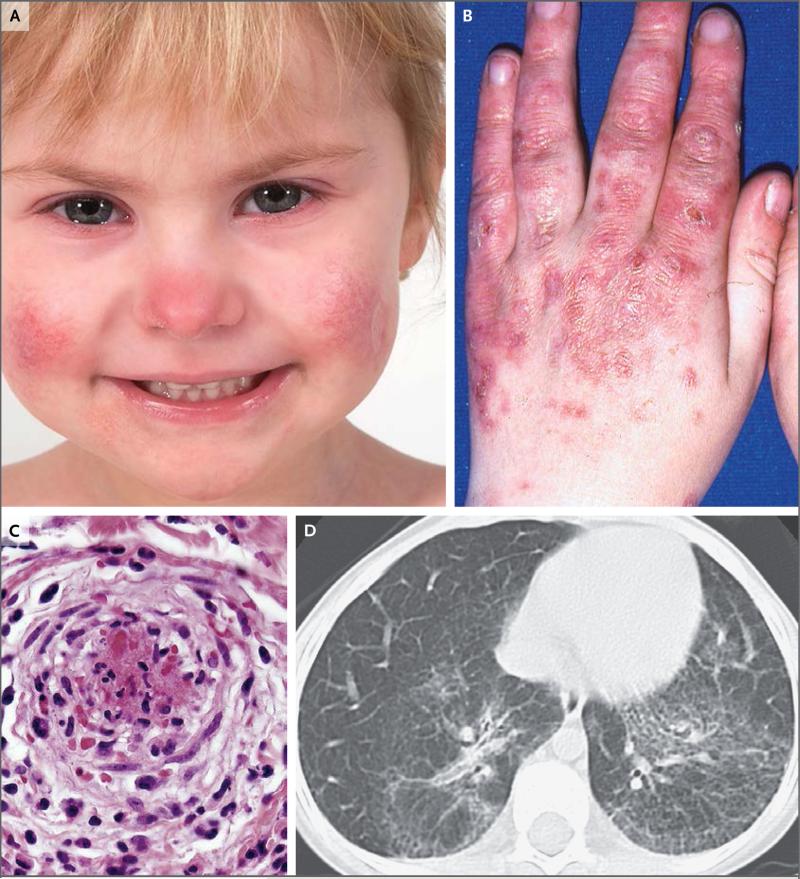
Figure 1. Clinical Features of Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING)–Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI).
Panel A shows the typical facial distribution of telangiectatic lesions on the nose and cheeks of Patient 1, who has SAVI. Panel B shows violaceous, scaling, atrophic plaques on the hands of Patient 6. Panel C shows histologic features of vascular inflammation in a skin-biopsy sample from a clinically involved area depicting a dense neutrophilic infiltrate with karyorrhexis throughout the vessel wall (hematoxylin and eosin); fibrin deposits are seen in the lumen of a severely damaged vessel. In Panel D, a high-resolution computed tomographic image of the lung of Patient 5 shows interstitial lung disease.