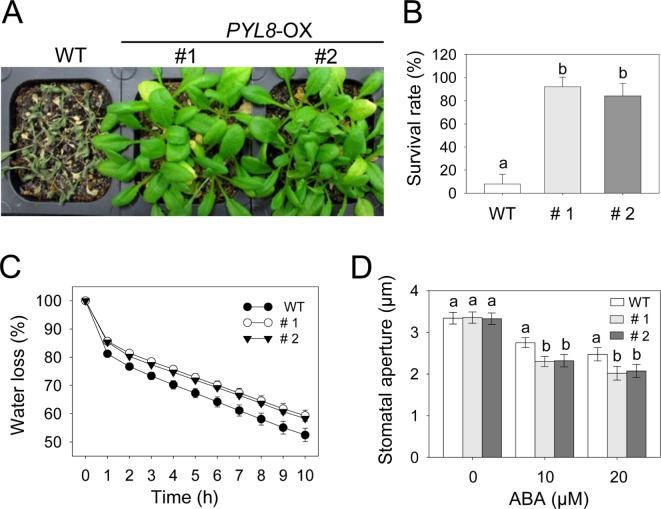
Fig. 2.
Enhanced resistance of PYL8-OX mutants to drought stress. (A) Growth of wild-type and PYL8-OX mutants after dehydration by water withholding for 14 d. (B) The percentage of surviving plants after dehydration for 14 d. Data are the means ± standard errors (n = 27). (C) Transpiration rates of wild-type and PYL8-OX mutant. Leaves of wild-type and transgenic plants were weighted at various times after detachment of leaves. Data are the means ± standard errors (n = 10). (D) ABA-hypersensitive stomatal closing in PYL8-OX mutants. Stomatal apertures were measured under the microscope in wild-type and PYL8-OX mutants. Data are the means ± standard errors (n = 80). Different letters indicate significant differences at p < 0.05 according to Duncan’s multiple range test.