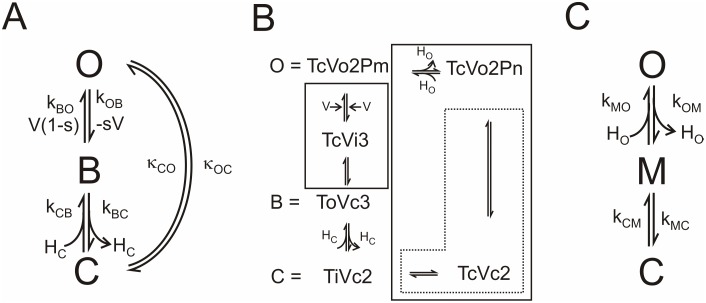
Figure 5. Reaction schemes for the dependence of proton transport in M2D44A on cytosolic pH.
(A) Cyclic reaction with the following states of the M2 protein. O: the external part of the protein has taken up a proton from the external side or is ready to release a proton to the external solution. B: the protein has bound a proton from O via the voltage-sensitive translocation kOB or from C (kCB) and is ready for the voltage-sensitive translocation of this proton to O (kBO) or release to C (kBC), C: the protein is ready to bind a cytosolic proton and transfer it to B with the rate constant kCB or to take a proton from B (kBC) and release it to the internal side. The recycling step O-C includes the resetting of the conformational changes of the protein necessary for the transport of the next proton. It also includes the exchange of a proton with the external solution. (B) Augmented model derived from the structural information as detailed in the Introduction. The meaning of the symbols is as follows: Capital letter: T = Trp41-basket; V = Val27-gate, P = pool in the cavity filled with m or n protons, m>n; small letter o = open, i = open, but instable c = closed; Number: Protonation state of the His37-box. The equality sign indicates which state of the augmented model is assigned to a state in the model in (A). The solid boxes include reactions, which are merged to gross reactions in (A) as explained in file S1. The dotted box indicates the gross reaction kMC and kCM used in the recycling branch of the model in (C). (C) The recycling pathway with the gross rate constants κOC and κCO of (A) is split up into two steps: O-M with external proton binding kMO (and release kOM), and recycling (M-C) with the gross rate constants kMC and kCM as indicated by the dotted box in (B).