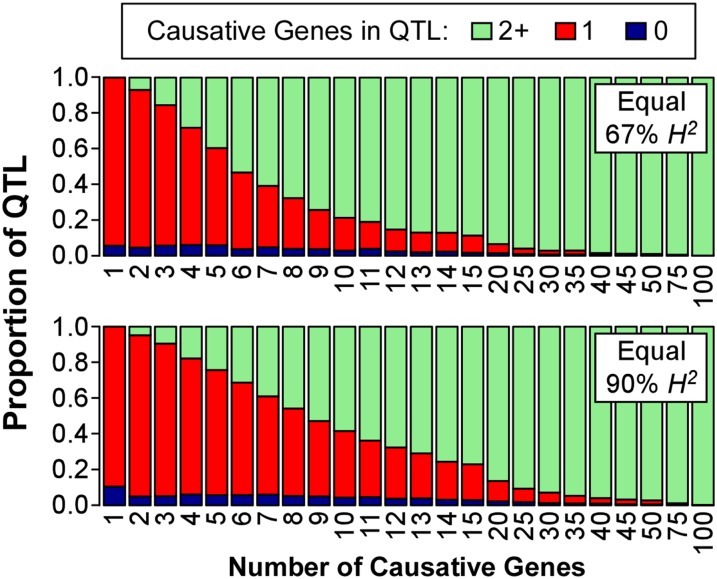
Figure 3.
The proportion of detected QTL with zero, one, or more than one simulated causative genes in the 1.5-LOD support interval. High numbers of causative genes lead to detected QTL that contain multiple causative genes. There is a reasonable percentage of detected QTL in the simulations that contain a single causative gene when few (less than four) causative genes are simulated, but as the number of simulated causative genes increases we quickly lose the power to distinguish between closely linked causative genes and they become lumped into single detected QTL. Equal-effect simulations shown here are very similar to those seen for the gamma-distributed effects (Figure S3).