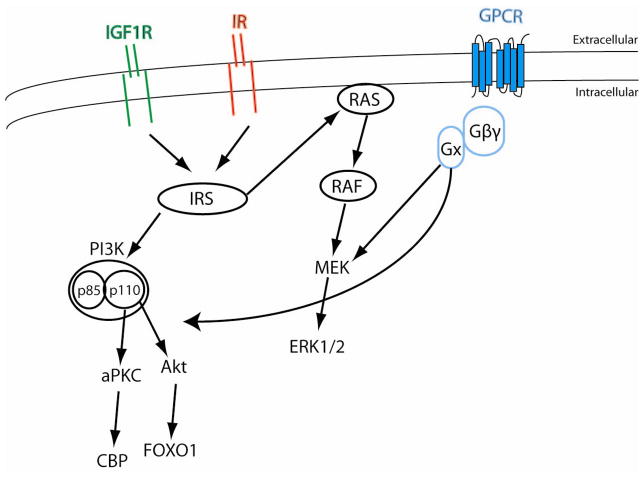
Figure 1. Common signaling pathways activated by insulin and IGF-1 receptors.
Both insulin and IGF-1 receptors are receptor tyrosine kinases. Receptor activation results in autophosphorylation of receptor which in turn can activate IRS1-4. IRS can activate the Ras GTPase. Ras induces sequential activation of Raf, MEK and ERK1/2. Activated IRS protein can also activate the regulatory subunit of the PI3-kinase, p85, which in turn stimulates the p110 catalytic subunit of PI3-Kinase. PI3-Kinase is a lipid kinase that induces an inositol phosphate cascade resulting in activation of Akt and the atypical PKC (aPKC). G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) is also indicated representing kiss1 receptor in the GnRH neuron or the GnRH receptor in the pituitary gonadotroph. Binding by ligand induces conformation changes that result in activation of an associated G-protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The α subunit of the G-protein complex (Gαx = Gαs, Gαi, Gαq) dissociates from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins (Gαs activates adenylyl cyclase, Gαi, inhibits adenylyl cylcase, Gαq activates phospholipase C. Both kiss1 and GnRH can activate canonical insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathways. CBP (CREB binding protiens) and FOXO1 represent potential intersecting nodes for insulin/IGF-1 signaling and GnRH signaling in the pituitary gonadotroph.