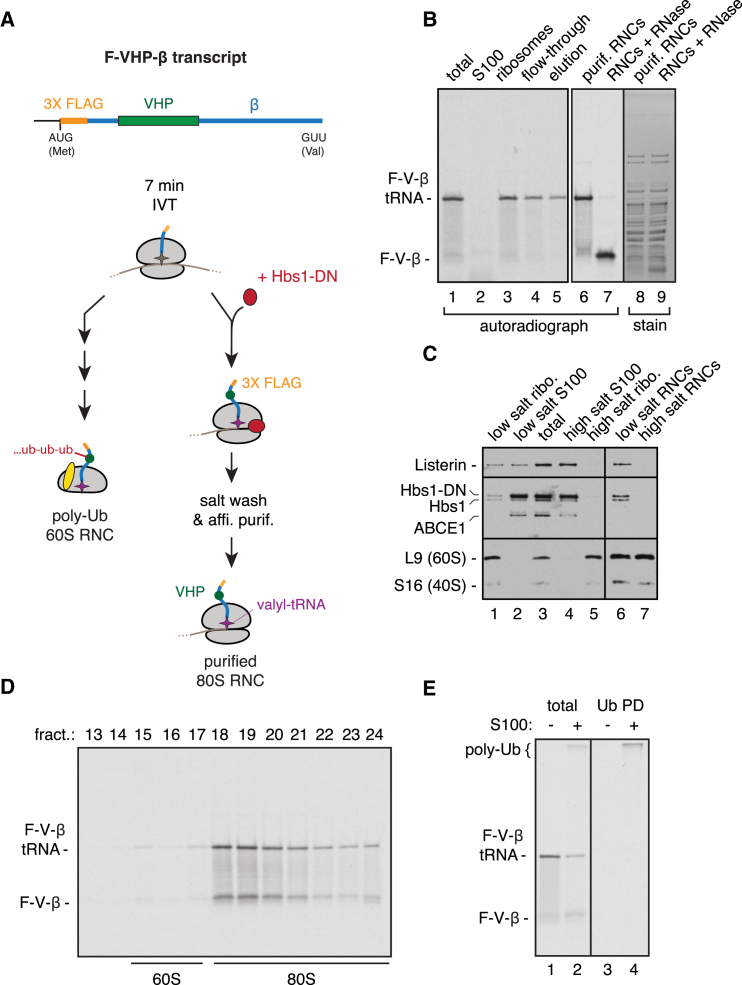
Figure 1.
Purified Stalled 80S RNCs Are Ubiquitinated In Vitro
(A) Scheme for purifying stalled 80S RNCs housing the model substrate F-VHP-β.
(B) F-VHP-β was in vitro translated with 35S-methionine and purified by the scheme in (A). Fractions during the purification were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The primary product contains an attached tRNA (F-V-β-tRNA), which is hydrolyzed by RNase to F-V-β (lane 7). Lanes 8 and 9 show Coomassie-blue-stained image of lanes 6 and 7, respectively.
(C) In vitro translation reaction of F-VHP-β (lane 3) was fractionated using physiologic or high-salt conditions (lanes 1–5) and affinity purified via the FLAG tag (lanes 6 and 7), as shown in (A). All fractions were immunoblotted for Listerin, Hbs1, ABCE1, and the ribosomal proteins L9 and S16. Endogenous Hbs1 and exogenously added Hbs1-DN are labeled.
(D) A 10%–30% sucrose gradient analysis of 35S-labeled F-VHP-β RNCs, purified as in (B), with positions of 60S and 80S indicated.
(E) Purified 35S-labeled F-VHP-β RNCs were subjected to ubiquitination reactions with or without S-100 derived from RRL. The total reaction products and ubiquitin pull-downs (Ub PD) via the His tag were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The unmodified substrate (F-V-β-tRNA) and poly-ubiquitinated (poly-Ub) products are indicated. (See also Figure S1.)