Figure 2.
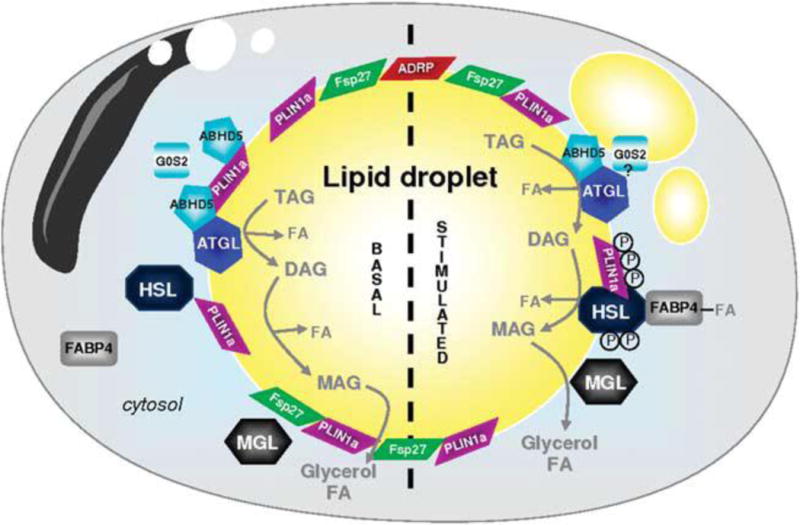
From: A Girousse and D Langin [110]
Adipocyte ‘lipolysome’ in basal and stimulated state. Lipid droplets (LDs) are surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer in which different proteins are anchored: PLIN1a (perilipin A), PLIN2 (ADRP) and Fsp27/Cidec. In the unstimulated basal state, ATGL, perilipin and ABHD5 are forming a complex at the surface of the LD. These protein interactions maintain ABHD5 inactive and as a consequence limit basal ATGL-mediated lipolysis. HSL and FABP4 are in the cytosol. In the stimulated state, HSL is phosphorylated by protein kinases (PKs); the active form of HSL migrates to the surface of the LD. PK also phosphorylate PLIN1a that undergoes structural modification and rearrangement leading to fragmentation of the LD. ABHD5 released from phosphorylated PLIN1a activates ATGL to initiate TAG hydrolysis. G0S2 can limit ATGL enzyme activity. DAGs are then transformed into MAG by active HSL. MGL ends the lipolytic process and releases glycerol and FA. FA-complexed FABP4 can interact with HSL to modulate lipolysis. ABHD5, abhydrolase domain containing; ADRP, adipose differentiation-related protein; ATGL, adipose triglyceride lipase; DAG, diacylglycerol; FA, fatty acid; FABP4, fatty acid-binding protein 4; Fsp27, fat-specific protein 27, also called Cidec; G0S2, G0/G1 switch gene 2; HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase; MAG, monoacylglycerol; MGL, monoglyceride lipase; PLIN1a, perilipin A; TAG, triacylglycerol.
