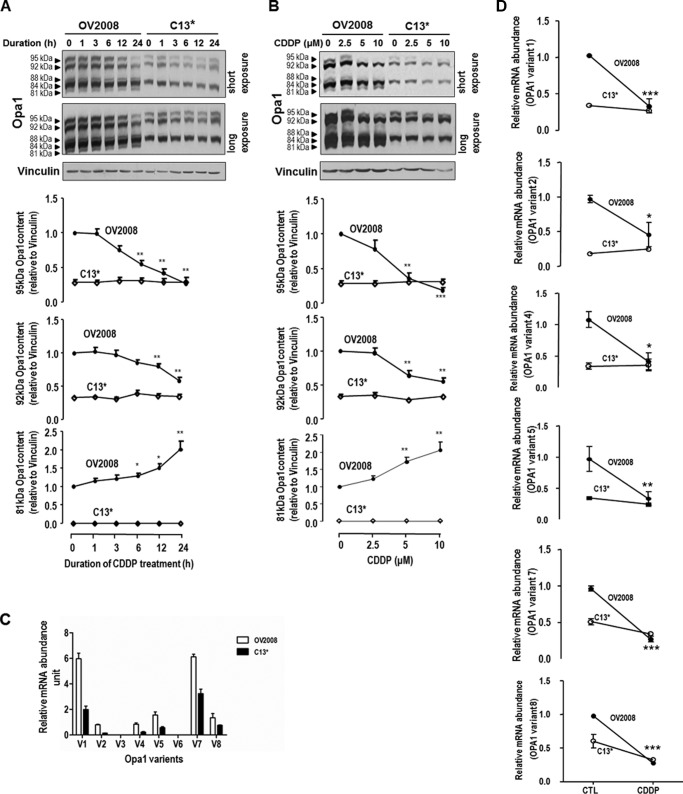
FIGURE 2.
Different forms of Opa1 in CECA cells. Chemosensitive (OV2008) and chemoresistant (C13*) CECA cells were cultured with CDDP for different durations (A; 10 μm, 0–24 h) or at different concentrations (B; 0–10 μm, 24 h). Contents of different forms of Opa1 and vinculin (loading control) were examined by Western blot. Five forms of Opa1 (95, 92, 88, 84, and 81 kDa) were recognized in OV2008 cells, whereas only three forms (95, 92, and 84 kDa) were recognized in C13* cells. CDDP significantly decreased contents of L-Opa1 forms (95 and 92 kDa), whereas it significantly increased S-Opa1 content (81 kDa) in a time-dependent (A; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, n = 4) and concentration-dependent (B; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001, n = 3) manner in OV2008 cells but not in C13* cells. C, OV2008 and C13* cells were cultured with CDDP (10 μm, 6 h; DMSO as control (CTL)), and the abundance of each Opa1 splice form was examined by quantitative PCR. Forms 1, 2, 4, 5, 7, and 8 were expressed in OV2008 and C13* cells, and the abundance of the above forms are higher in OV2008 cells than C13* cells (p < 0.05, n = 3). V with a number represents specific form of Opa1. D, CDDP decreased all Opa1 splice forms detected in OV2008 cells, not in C13* cells (p < 0.05, n = 3).