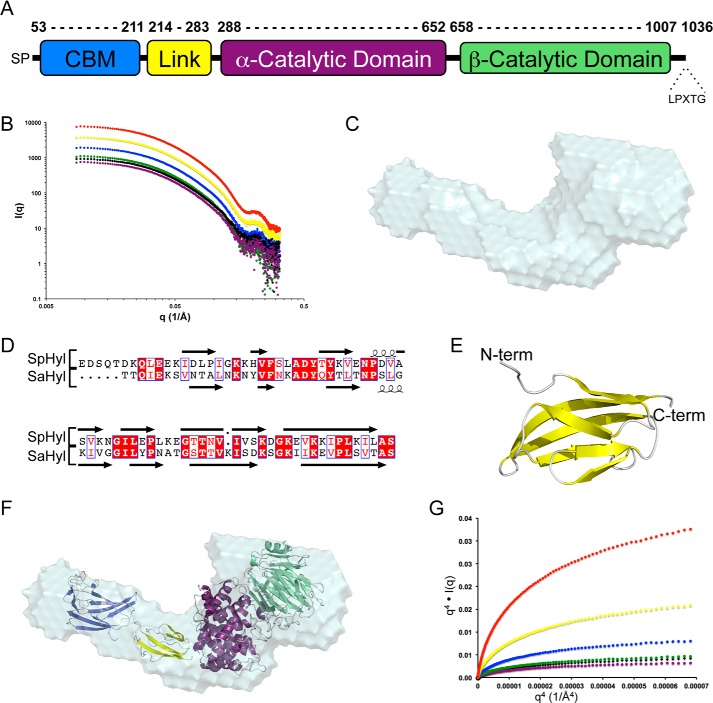
FIGURE 3.
Modular properties and initial SAXS analysis of full-length Hyl. A, schematic of the modular architecture of Hyl. The α- and β-catalytic domains constitute the PL8 domain. B, SAXS scattering profiles of Hyl, protein concentrations: 10.80 (red), 5.40 (yellow), 2.70 (blue), 1.50 (green), 1.35 (black), and 1.00 mg/ml (purple). C, DAMAVER averaged shape of 10 independent DAMMIF-generated envelopes of Hyl using the data collected on the 1.0 mg/ml sample. D, alignment of the linker module from Hyl with the similar module from the Streptococcus agalactiae Hyl (SaHyl). E, Phyre2-generated model using the structure of the SaHyl linker domain as a template. F, the composite modules of Hyl (CBM (blue), linker (yellow), α-catalytic domain (purple), and β-catalytic domain (green)) manually placed into the DAMMIF envelope. G, Porod-Debye plots of the SAXS data for Hyl. A, q4·I(q) versus q4 plot for Hyl at 10.80 (red), 5.40 (yellow), 2.70 (blue), 2.4 (green), 1.35 (black), and 1.00 mg/ml (purple).