FIGURE 3.
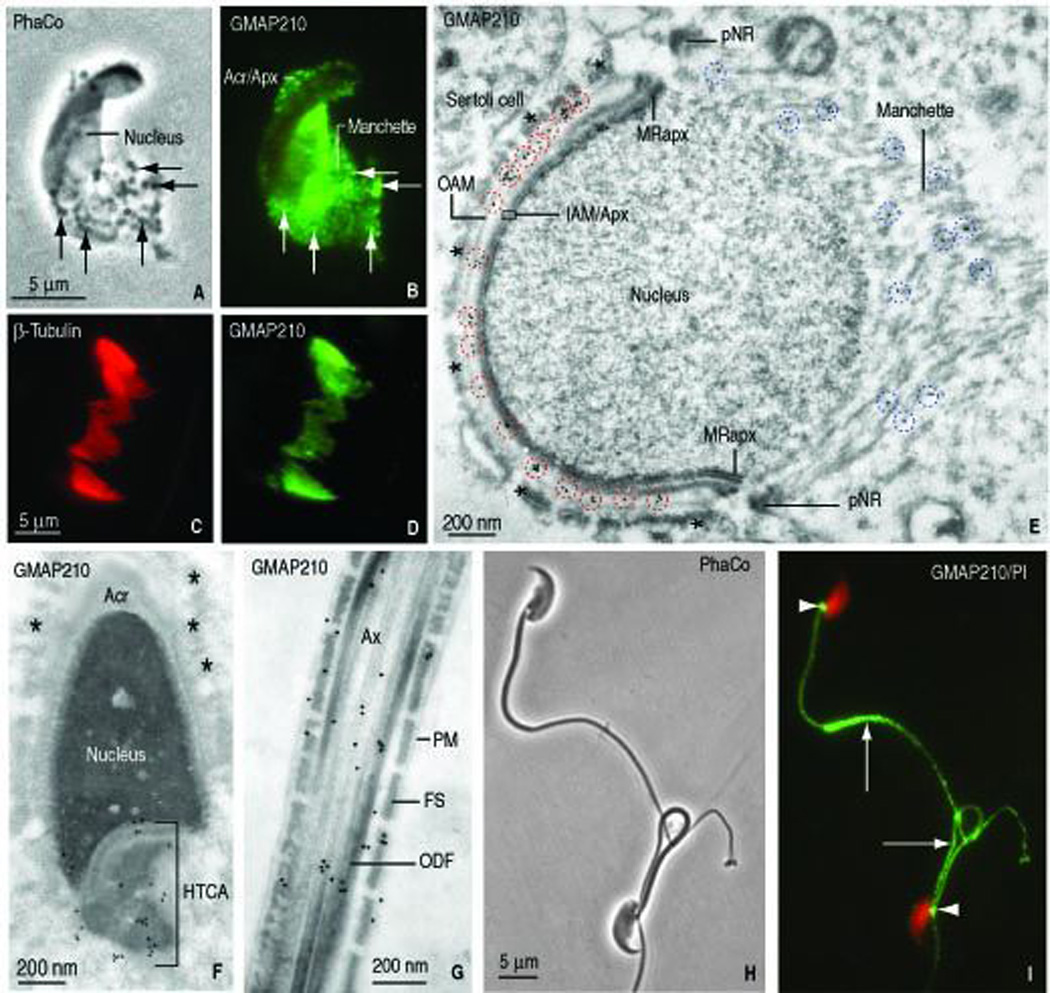
Localization of GMAP210 in elongating spermatids and fractionated manchettes (rat) and epididymal sperm (mouse). A. Phase contrast microscopy of an elongating rat spermatid (panel A, PhaCo; step 10) shows an elongating head and the associated manchette with granular material (arrow). B. GMAP210 immunofluorescence is seen in the acrosome-acroplaxome (Acr/Apx) and the manchette. The Golgi has already migrated to the caudal cytoplasmic region of the spermatid (not shown). C–D. β-tubulin and GMAP210 stained fractionated manchettes from rat spermatids. E. Immunogold electron microscopy localization of GMAP210 along the outer acrosome membrane (OAM), the inner acrosome membrane-acroplaxome interface (IAM/Apx) and microtubules of the manchette. pNR, perinuclear ring of the manchette. MRapx, marginal ring of the acroplaxome. The blue dashed circles denote the localization of GMAP210 in the manchette; the red dashed circles emphasize the localization of GMAP210 on the acrosome membranes. The asterisks indicate bundles of F-actin in the apical ectoplasmic region of a Sertoli cell. The bundles are closely apposed to the elongating acrosome-acroplaxome-nucleus. F. Elongating spermatid (rat, step 16). GMAP210 is localized in the head-tail coupling apparatus (HTCA) but not along the acrosome (Acr) membranes and the subjacent acroplaxome. The asterisks indicate bundles of F-actin in an adjacent Sertoli cell. G. Principal piece of the tail of an elongating spermatid. GMAP210 is seen along the axoneme (Ax), outer dense fibers (ODF) and portions of the fibrous sheath (FS). PM, plasma membrane. H. Epididymal mouse sperm (phase contrast microscopy, PhaCo). I. GMAP210 is not visualized in the sperm head but is seen in the HTCA (arrowheads) and the tail (arrows).
