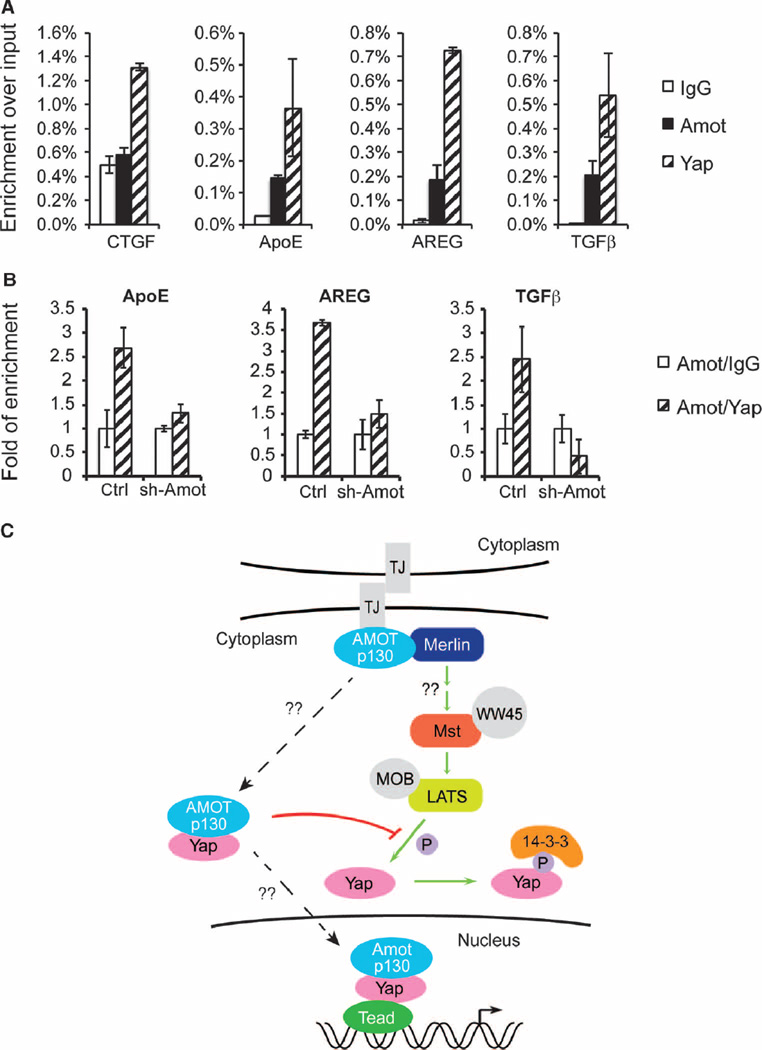
Fig. 7. Amot associates with a chromatin-bound Yap-Tead transcriptional complex.
(A) ChIP with IgG, Amot, or Yap antibody in HEK293 cell lysates, followed by real-time qPCR analysis of the promoter regions of ApoE, AREG, TGFB1, and CTGF. Enrichment of each product was calculated relative to input. Data are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. (B) Sequential ChIP with Amot antibody followed by IgG or Yap in control and Amot-KD HEK293 cell lysates, followed by real-time qPCR analysis of the promoter regions of ApoE, AREG, and TGFB1 genes. The fold of enrichment of each product with Yap antibody was calculated relative to IgG after Amot ChIP. Data are means ± SEM from three independent experiments. (C) Schematic representation of the multiple interactions of Amot with Merlin-Hippo-Yap signaling in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. In this model, Amot-p130 prevents Yap-Lats1/2 (LATS) interaction in the cytoplasm and LATS-mediated Yap phosphorylation. Subsequently, the Amot-p130/Yap complex translocates to the nucleus to regulate Tead-target gene transcription. TJ, tight junction.