Figure 2.
Gene Expression Variability Is Concordant with Network Connectivity
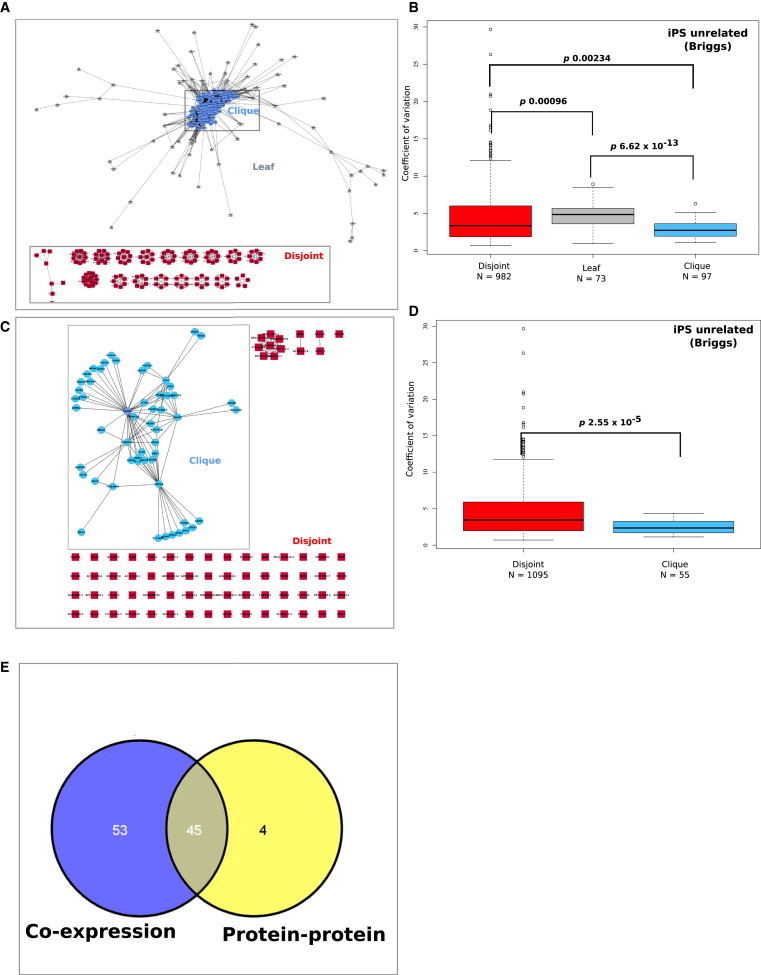
(A) Coexpression network derived from iPS unrelated (Briggs) data set. An edge A→B is drawn whenever there is a correlation in average log2 expression greater than or equal to 0.995. Identifiable substructures were arbitrarily defined as the clique, leaf, and disjoint regions. The color of each node reflects the region to which it has been assigned.
(B) CoV profiles for each region in the coexpression network in the iPS unrelated (Briggs) data set. The x axis describes the network regions and y axis describes the coefficient of variation. The p values assess significant differences in gene expression variability between each network region (p, 0.05, Wilcoxon rank sum).
(C) Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network derived from genes in the full coexpression network using the BisoGenet plug-in for Cytoscape. An edge A→B is drawn whenever there is experimental data that validates an interaction between the protein products of each gene. The densely connected region (defined as the clique) clearly separated from the other nodes (defined as disjoint); no leaf nodes were produced in this network.
(D) CoV profiles for each region in the PPI network in the iPS unrelated (Briggs) data set. The p values assess significant differences in gene expression variability between each network region (p, 0.05, Wilcoxon rank sum).
(E) Venn diagram illustrates the overlap between genes in the coexpression and protein-protein interaction networks for the clique region.
