Figure 11.
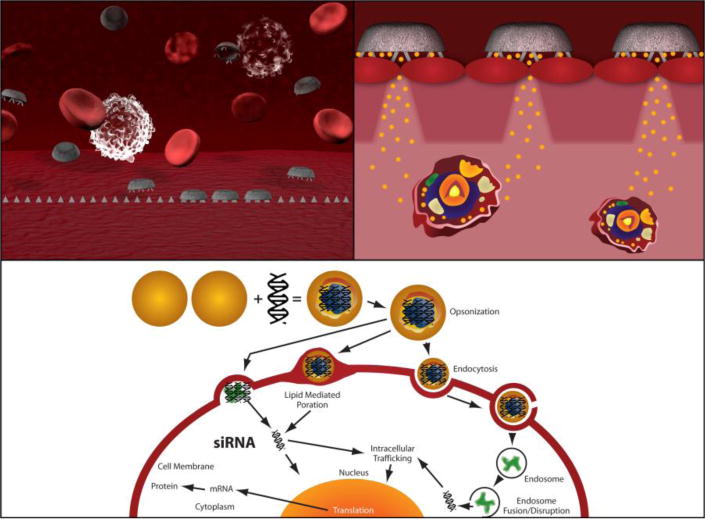
Mechanism of action of multistage (3rd generation) nanovectors. Top-left: rationally designed stage one particles marginate to the vessel wall and adhere to the endothelium. Top-right: stage one particles release a penetration enhancer to break down tight junctions and the basement membrane and release stage two particles – in this instance, liposomes. Bottom: the stage two liposomes interact with the target cell membrane, and then deliver the intended payload – in this example, siRNA. Reprinted with permission.[151]
