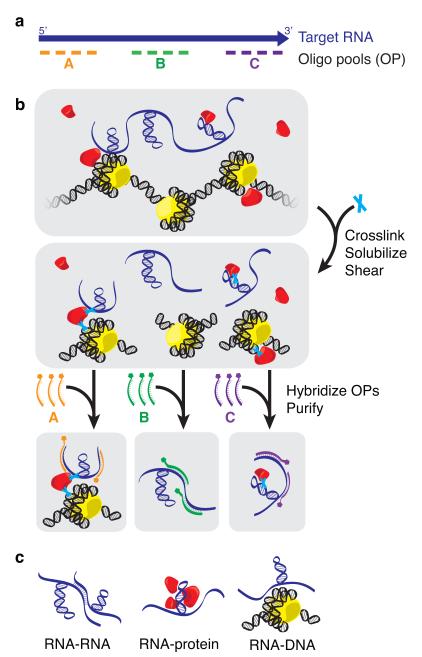
Figure 1.
dChIRP uses antisense oligos to purify specific RNA domains and associated RNAs, proteins, and chromatin. (a) dChIRP oligo design strategy. Biotinylated antisense oligos are designed to tile specific regions of the target RNA. (b) dChIRP workflow. To prepare chromatin, whole cells are cross-linked to preserve protein-nucleic acid interactions. Sonication is used to solubilize the nuclear fraction and shear nucleic acids. Next, the chromatin is subdivided into equal samples. OPs are added to each sample, which hybridize to the targeted RNA fragments. The biotinylated oligos, RNA targets, and cross-linked biomolecules are then purified on magnetic streptavidin beads, and unbound material is washed away. (c) RNA-, protein-, and DNA-sensitive modalities of dChIRP. RNA, protein, and DNA fractions are extracted from each dChIRP sample. Intra- or inter- molecular RNA-RNA, RNA-protein, and RNA-DNA interactions may be measured by RT-qPCR, immunoblotting, and qPCR or sequencing, respectively.