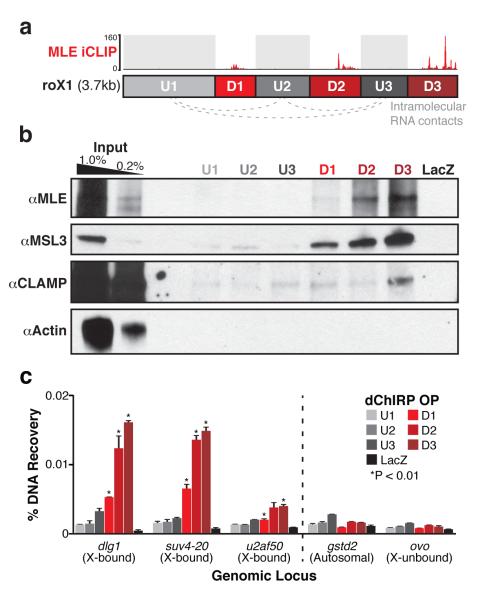
Figure 3.
roX1 D domains interact with the MSL complex and chromatin on the X. (a) Schematic representation of roX1 interactions. The three D domains (D1, D2, and D3) directly contact MLE by iCLIP18. The three intervening U domains do not contact MLE, but are topologically associated (gray dotted lines). (b) dChIRP-Western blot confirms known MLE-bound domains of roX1. The protein fraction from each roX1 dChIRP sample was analyzed by immunoblotting against MLE, MSL3, CLAMP, and Actin. roX1 domains D1, D2, and D3 efficiently recovered MLE and MSL3 proteins. D3 recovered more protein than D2, and D2 recovered more than D1. Domains U1, U2, and U3 recovered minimal or undetectable MLE and MSL3. Only D3 recovered CLAMP appreciably, albeit very weakly. LacZ ChIRP recovered no detectable protein. Actin was not detected in any sample. (c) The three D domains of roX1 are associated with chromatin at dosage compensated loci on the X chromosome. DNA fractions from each roX1 dChIRP sample were analyzed by qPCR and normalized to input. Five genomic loci were investigated: three MSL-bound X-linked loci (dlg1, suv4-20, u2af50), one locus from an autosome (gstd2), and an unbound X-linked locus (ovo). dChIRP of domains D1, D2, and D3 significantly enrich for X-bound loci relative to control loci (*P-value < 0.01, t-test). Domains D2 and D3 recover significantly more X-bound DNA than D1 or the three U domains. LacZ ChIRP fails to recover substantial DNA from any locus. Average of technical triplicates +s.d. shown.