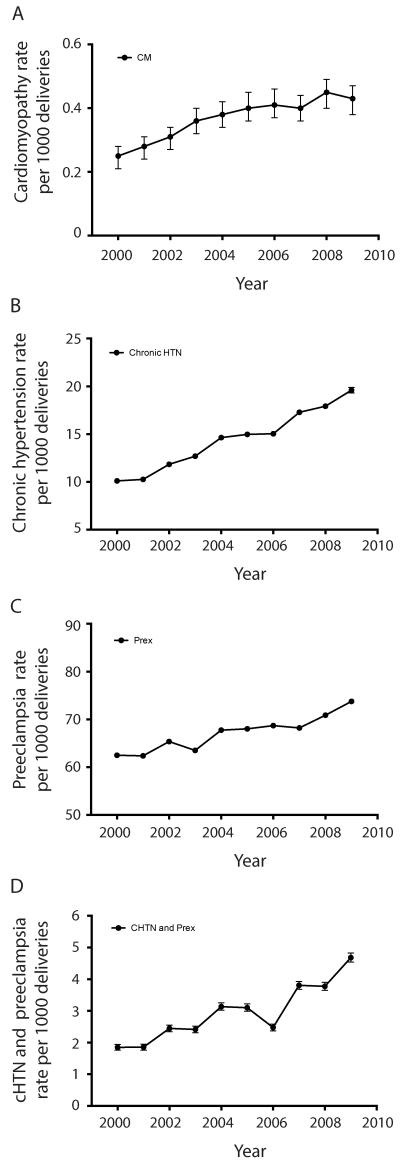
Figure 1. Trends in the prevalence of cardiomyopathy, chronic hypertension, preeclampsia, and chronic hypertension with preeclampsia at delivery admissions, the 2000 – 2009 Nationwide Inpatient Sample (n = 43,226,239).
Error bars demonstrate 95% confidence intervals. A. There was an increase in the linear trend for cardiomyopathy diagnosed at delivery admissions during the 10-year study period (p<0.001, R2=0.90), increasing from 0.25 cases per 1000 deliveries in 2000 to 0.43 per 1000 deliveries in 2009. B and C. There was an increase in the linear trend for chronic hypertension (B. p<0.001, R2=0.99) and preeclampsia (C. p<0.001, R2=0.90), increasing from 10.1 per 1000 deliveries in 2000 to 19.6 per 1000 deliveries in 2009, and from 62.5 per 1000 deliveries in 2000 to 74.0 per 1000 deliveries in 2009, respectively. D. There was an increase in the linear trend for chronic hypertension with preeclampsia (D. p<0.001, R2=0.84), increasing from 1.8 per 1000 deliveries in 2000 to 4.7 per 1000 deliveries in 2009.