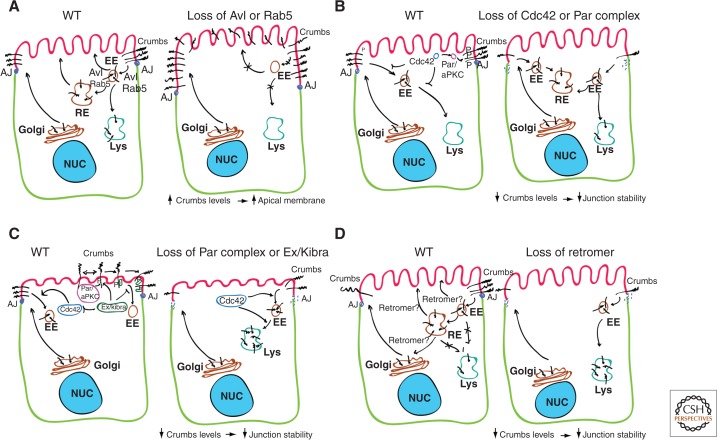
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms for Crumbs endocytic and recycling regulation in epithelial cells. (A) Apical Crumbs is endocytosed from the apical surface via Avl and Rab5 to the early endosome (EE), to maintain the level of surface expression of Crumbs that allows appropriate overall apicobasal polarity. From the EEs, Crumbs is then recycled back to the plasma membrane or degrades in lysosomes. Biosynthetic transport of Crumbs also contributes to maintain its appropriate levels in the apical surface. When endocytosis is blocked through the loss of Avl or Rab, Crumbs accumulates on the cell surface, leading to mispolarization of the cell. (B) Cdc42 and the Par complex prevent the endocytosis of Crumbs from the apical plasma membrane in the Drosophila neuroectoderm. Loss of Cdc42 or the Par complex induces Crumbs endocytosis and AJs disorganization. Cdc42 also prevents lysosomal degradation of Crumbs. (C) In the Drosophila follicle cell epithelium, Crumbs–Crumbs interaction via the extracellular domain of Crumbs facilitates aPKC phosphorylation and stabilization of the entire apical complex at the plasma membrane by preventing Crumbs endocytosis. Ex and Kibra associate with phosphorylated Crumbs at the FERM domain and function to maintain Crumbs at the plasma membrane. Ex/kibra also inhibits Cdc42, which promotes the lysosomal degradation of Crumbs. (D) Retromer is responsible for sorting Crumbs at the early sorting endosome for recycling, away from the degradative pathway. Crumbs recycling pathways could be from the EE, the recycling endosome (RE), or the trans-Golgi network (TGN).