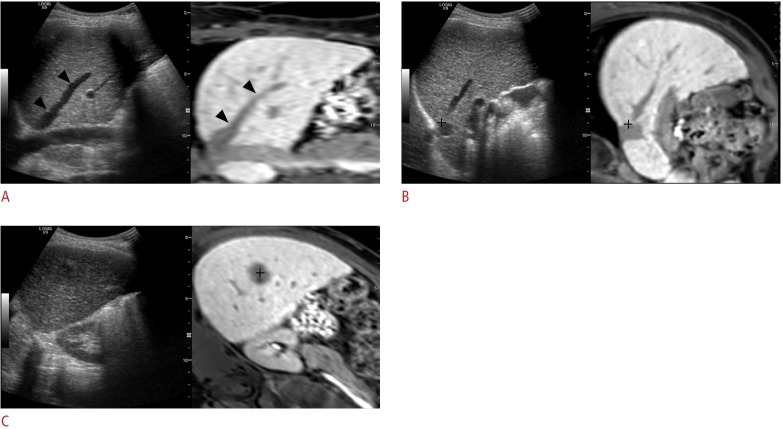
Fig. 1. The process of image fusion between real-time ultrasonography (US) and magnetic resonance (MR) images by using internal markers.
A. Uploaded MR data are processed in the US machine and are displayed in the coronal plane (right figure) in the US monitor. The US image (left figure) is also scanned along the coronal plane that shows similar anatomic structures. Arrowheads indicate the right hepatic vein, and this vein was used as the anatomic landmark for plane registration. B. For the calibration of image fusion, point registration is performed by placing the cursor (cross marker) at the same anatomic structure. In this example, the bifurcation point of the inferior vena cava and the right hepatic vein was used for point registration. C. After plane and point registrations, the target lesion usually appears at a similar location of each image. Then, point registration is added by placing the cursor at the center (cross marker) of the tumor.