Fig. 7. Fusion imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (US)-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of a subcentimetersized recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in a patient with a hepatitis B virus carrier. The patient had previously undergone percutaneous RFA of HCC.
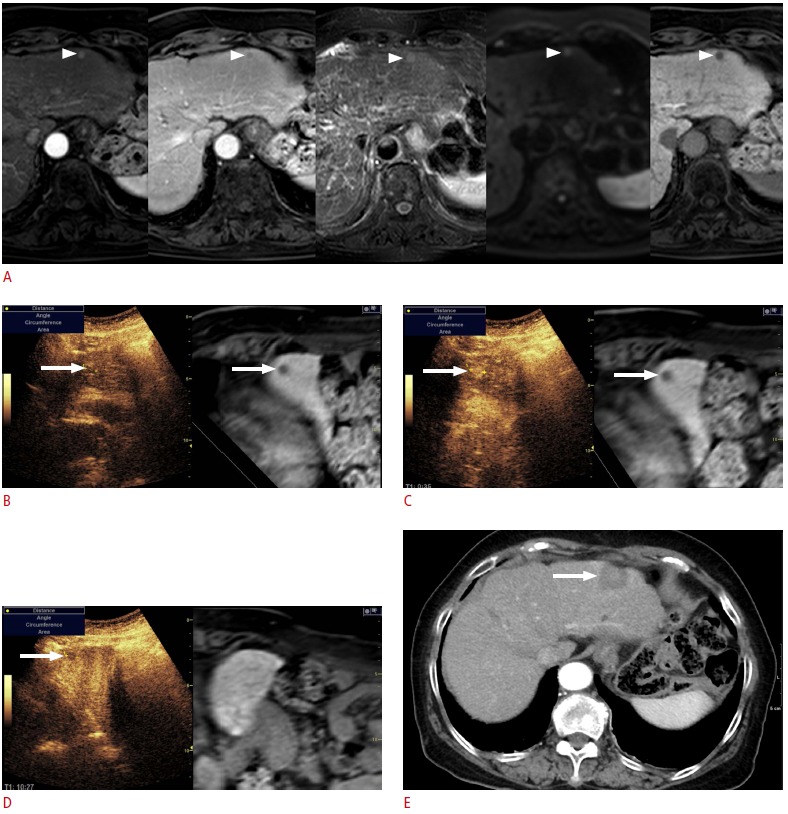
A. In the magnetic resonance (MR) images (arterial phase, followed by portal phase, T2-weighted image, diffusion-weighted image, and hepatobiliary phase), the lesion (arrowheads) shows the typical imaging features of HCC. Although the size of the lesion was measured to 0.8 cm, it was regarded as a recurrent HCC since it was a new lesion, not seen in the previous computed tomography or MR images. B. To be certain, contrast-enhanced US was performed in addition to the fusion imaging. On the scout image, the lesion (arrow) was identified at the same location where the index tumor (arrow) was located on the fused MR image. C. In the arterial phase, the lesion (arrow) shows strong enhancement. D. In the Kupffer phase, the lesion (arrow) is seen as a defect, indicating that the lesion is an HCC. E. Immediate post-RFA computed tomography scan shows that the tumor was completely covered by the ablation zone (arrow), suggestive of technical success.
