Figure 5.
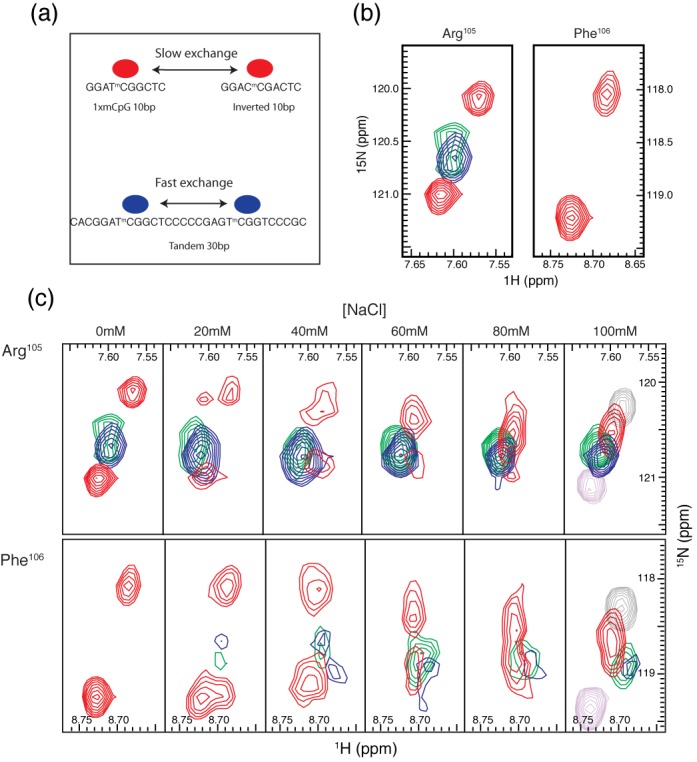
MBD4MBD exchanges between methylated sites in the same molecule of DNA on the fast NMR timescale. (a) A diagram depicting slow intermolecular and fast intramolecular exchange by MBD4MBD. (b) 2D 1H-15N TROSY HSQC spectra of MBD4MBD bound to methylated wild-type and inverted (10 bp) DNA (red), tandem (30 bp) DNA (blue) and tandem nicked (30 bp) DNA (green) show that MBD4MBD more rapidly exchanges between sites in the same molecule of DNA. The spectra show only a single crosspeak for Arg105 (left panel) when bound to DNA containing both wild-type and inverted sites, which is consistent with fast intramolecular exchange. A similar comparison for Phe106 (right panel) shows marked broadening of the intramolecular crosspeaks consistent with intermediate exchange on the NMR timescale which likely reflects line-broadening from additional internal dynamic motions. Incorporating a single-strand defect does significantly alter rapid intramolecular exchange. (c) In contrast, increasing NaCl concentration accelerates both intermolecular and intramolecular exchange. The two separate peaks reflective of intermolecular exchange (red) for both Arg105 (upper panels) and Phe106 (lower panels) coalesce into a single peak with increasing NaCl concentration. This change indicates that the intermolecular exchange rate has increased from the slow to fast NMR timescale. Likewise the crosspeaks reflective of intramolecular exchange (blue and green) sharpen with increasing NaCl concentration, which is consistent with accelerated intramolecular exchange. For comparison, 2D1H-15N TROSY HSQC spectra of MBD4MBD bound to methylated wild-type (gray) and inverted (purple) DNA are shown at 100 mM NaCl.
