Figure 4.
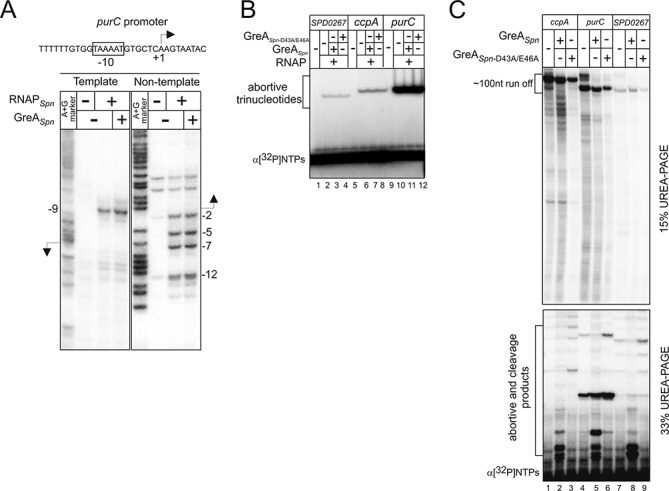
Transcription initiation and promoter escape are not influenced by GreASpn. (A) Open complexes of the purC promoter formed by RNAPSpn in the presence or absence of GreASpn were probed with KMnO4. A + G reaction was used as a marker. (B)In vitro abortive initiation on ccpA, purC and SPD_0267 with or without GreASpn or mutant GreASpn-D43A/E46A. (C). Products of in vitro transcription on short (resulting in ∼100 nt-long run off) ccpA, purC and SPD_0267 with or without GreASpn or mutant GreASpn-D43A/E46A were separated on 15 and 33% denaturing gels to visualize run off and abortive products, respectively. Short cleavage products at the bottom of the gel in the presence of GreASpn originate from cleavage in elongation complexes, as no cleavage is seen in the abortive initiation assay (panel B). Additional low mobility bands in the presence of GreASpn are thought to be cleavage products of the longer transcripts, in particular the full length ones that are known to be retained in the elongation complex at the ends of templates. Note that pauses in the presence or absence of GreASpn-D43A/E46A are similar and the apparent differences are attributed to the contrast of the image.
