Figure 1.
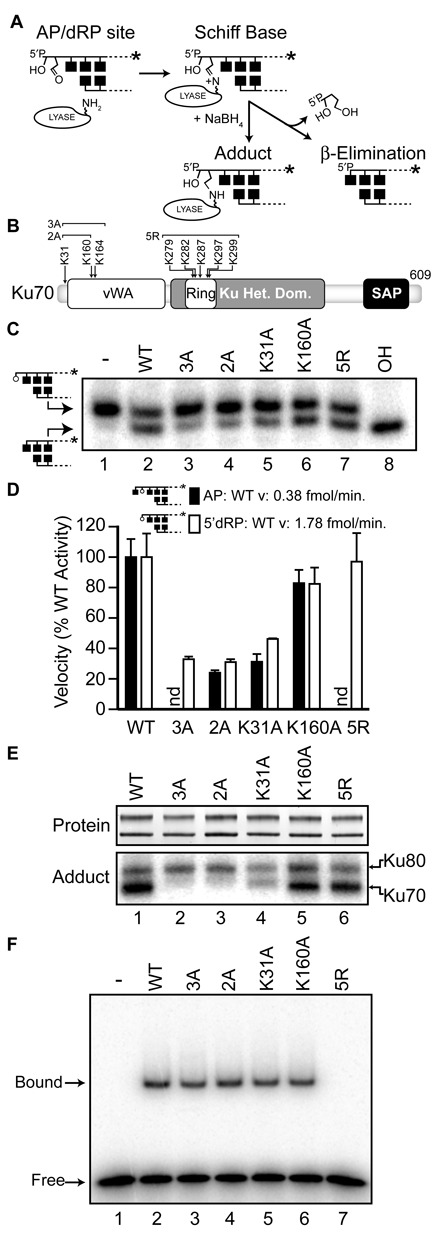
Identification of adducting lysines within human Ku70. A. Description of the 5′dRP/AP lyase reaction with abasic site, and use of NaBH4 to trap the covalent intermediate. B. Domain map of human Ku70 showing the location of lysines or groups of lysines that were mutated to alanine (A) or arginine (R). vWA, von Willebrand factor type A domain; SAP, SAF-A/B, Acinus and PIAS. C. Representative reactions were performed with 1 nM radiolabeled 5′dRP substrate with 5 nM purified recombinant Ku heterodimer at 37°C for 5 min, with the Ku70 subunit either WT or mutated as described in panel B. Reactions were analyzed by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). In lane 8 substrate was treated with alkali (OH) to validate abasic site generation. D. Average lyase velocities were determined by incubating 5 nM purified recombinant Ku heterodimer and 1 nM AP (filled bar) or 5′dRP (open bar) substrates at 37°C, and expressed as a percentage of the velocity observed with WT heterodimer. Error bars are the standard deviation of triplicate determinations. E. Purified heterodimers were subjected to sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS)-PAGE (SDS-PAGE) analysis and detected directly by SYPRO orange (top panel). Products of Schiff-base trapping assays (bottom panel) were detected by phosphorimaging after incubation of the heterodimer with radiolabeled 5′dRP substrate as in panel C, except reactions were supplemented with 5 mM NaBH4 and incubated for 10 min. F. EMSA was performed by incubating 1nM Ku with 1 nM radiolabeled 30 bp substrate for 15 min.
