Figure 6.
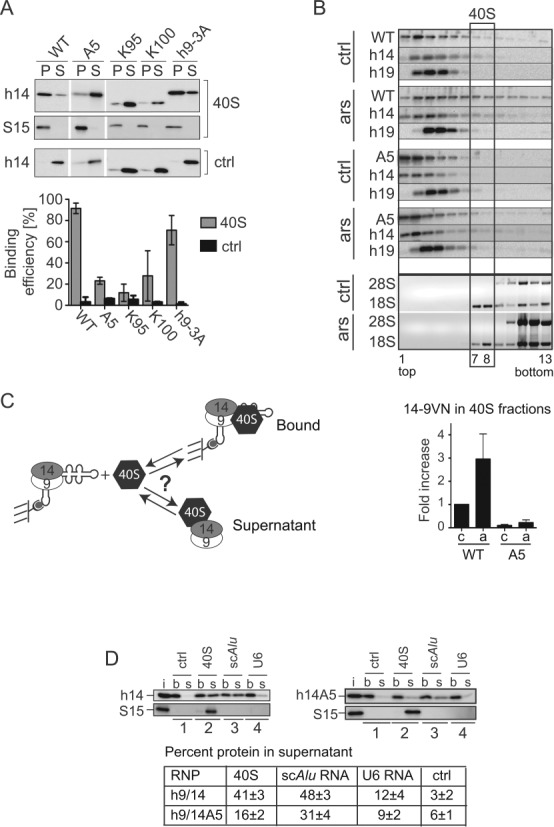
SRP9/14 binds to 40S subunits and cannot bind Alu RNA and 40S subunits simultaneously. (A) Binding of WT and mutated h9/14 to 40S. Equal amounts (100 nM) of purified recombinant proteins and purified rabbit 40S ribosomal subunits were incubated in a buffer containing 150 mM potassium acetate and 1.5 mM magnesium acetate. 40S-bound and free proteins were separated on sucrose cushions. Pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions were analyzed by Western blots (upper panel) and the results quantified (lower panel). K100 and K95 proteins were truncated at positions 100 and 95 in h14, respectively (see Figure 4D) (9,10). Ctrl: without 40S. Error bars are shown as SD, n ≥ 2. (B) Velocity sedimentation fractionation on 10–40% sucrose gradients of postnuclear supernatants obtained from HEK 293T cells expressing 14-9VN and 14-9VNA5. Western blots of gradient fractions with anti-h14 and anti-h19 antibodies. Bottom panels: agarose gels of RNA samples stained with ethidium bromide. ars: 500 μM sodium arsenite for 40 min; ctrl: untreated cells. Lower panel: relative amounts of the proteins 14-9VN and 14-9VNA5 present in fractions 7–8 as compared to untreated cells expressing 14-9VN (upper panel). Error bars are shown as SD, n ≥ 3. (C) Schematic representation of the protein transfer assay (PTA). Purified scAlu RNP is captured on magnetic streptavidin beads and purified 40S added in a buffer containing 150 mM potassium acetate and 5 mM magnesium acetate. Immobilized Alu RNP (b) is separated from the supernatant (s) after 5 min. (D) Western blots of the fractions from PTA experiments using anti-S15 and anti-h14 antibodies. Left panel: WT h9/14. Right panel: h9/14A5. Lane 1: mock control; lane 2: 40S; lane 3: nonbiotinylated scAlu RNA; lane 4: nonbiotinylated U6 RNA. (i): aliquots of h9/14 and 40S equivalent to the amounts loaded on the beads. Lower panel: quantification of the results.
