Figure 3.
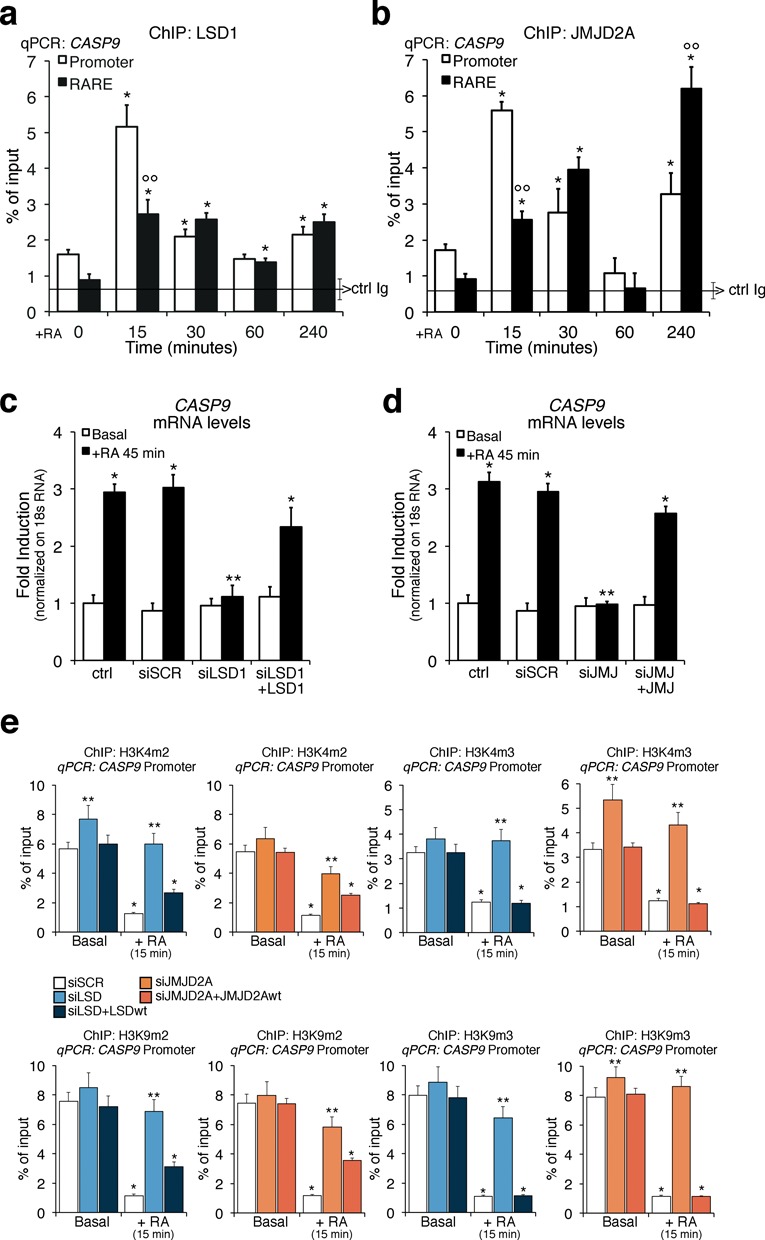
LSD1 and JMJD2A upon RA exposure are recruited to the CASP9 promoter and RARE sites and are essential for CASP9 induction by RA and methylation–demethylation cycle. (a, b) Recruitment of LSD1 and JMJD2A to the promoter and RARE of CASP9 gene. MCF7 cells were serum starved and exposed to 300-nM RA at the indicated times (15, 30, 60 and 240 min). qChIP was carried out using specific antibodies recognizing LSD1 and JMJD2A. The panels show the time course of the recruitment of LSD1 (a) and JMJD2A (b) to the RARE and promoter sequences of CASP9 analyzed by qPCR. The black, horizontal line in each plot indicates the percent of input from a control ChIP (Ab: non-immune serum). (c, d) LSD1 and JMJD2A depletion inhibits RA-induced transcription of CASP9. MCF7 were transiently transfected with LSD1 siRNA or JMJD2A siRNA. After 48 h, total RNA was prepared from control cells (starved) or RA-induced cells (300-nM RA for 45 min) and analyzed by qPCR with specific primers to CASP9 mRNA. The statistical analysis derives from at least three experiments in triplicate (n ≥ 9; mean ± SD); *P < 0.01 (matched pairs t-test) compared to RA-unstimulated sample; **P < 0.01 (student t-test): comparison between SCR and specific siRNAs; °°P < 0.01 (student t-test): comparison between promoter and RARE regions. (e) Depletion of LSD1 or JMJ2DA inhibits the methylation changes induced by RA. qChIP was performed on cells transfected with LSD1 siRNA or JMJD2A siRNA and induced with 300-nM RA for 15 min. qChIP was carried out using specific antibodies recognizing H3K4me3, H3K4me2, H3K9me3 and H3K9me2. The statistical analysis derives from at least three experiments in triplicate (n ≥ 9; mean ± SD); *P < 0.01 (matched pairs t-test) compared to RA-unstimulated sample; **P < 0.01 (student t-test): comparison between SCR and specific siRNAs. Transfection efficiency was monitored by FACS (Alexa Fluor or co-transfected pEGFP Vector).
