Figure 5.
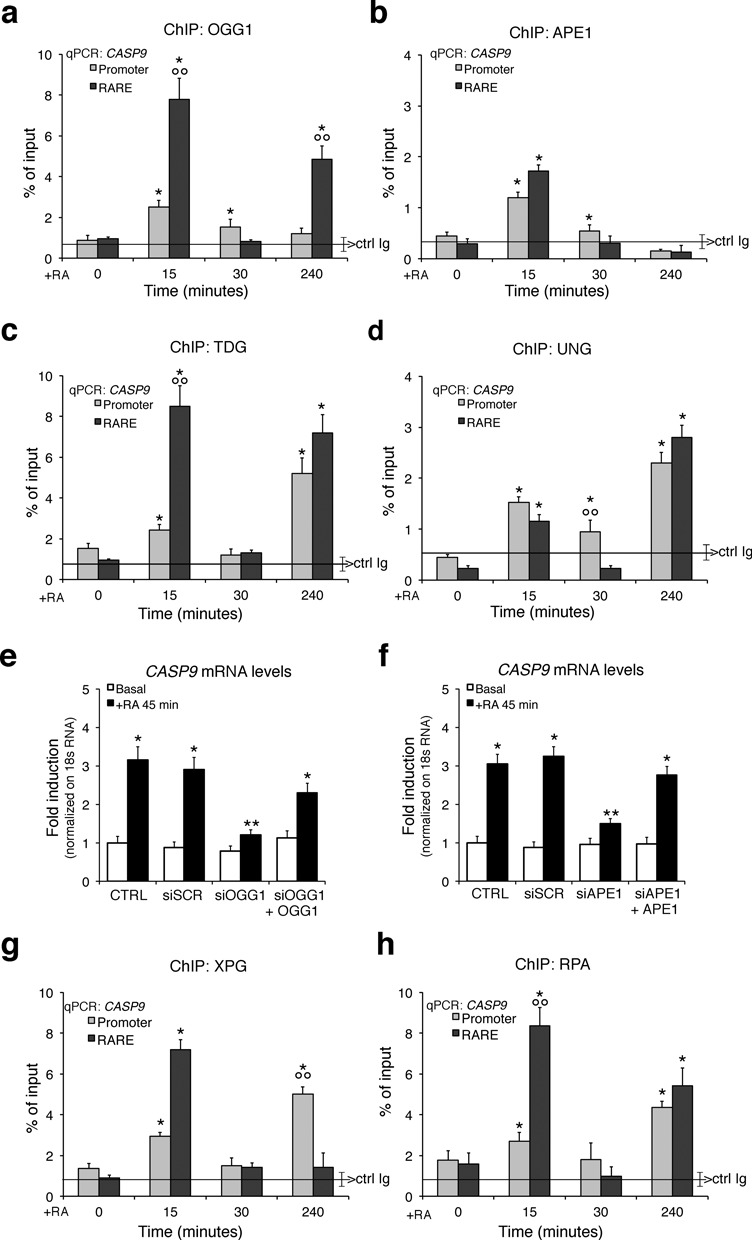
Recruitment of BER and NER enzymes to CASP9 chromatin following RA induction. MCF7 cells, starved or treated with RA for 15, 30 and 240 min, were analyzed by qChIP using specific antibodies recognizing the 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase-1 (OGG1), AP endonuclease (APE1), Thymine-DNA glycosylase (TDG), Uracil-DNA glycosylase (UNG), XPG and RPA. (a, b) The recruitment of OGG1 and APE1 to the CASP9 promoter, and RARE sequences. (c, d) The recruitment of TDG and UNG to the same regions of CASP9. The black, horizontal line in each plot indicates the percent of input from a control ChIP (Ab: non-immune serum). (e, f) BER knockdown impairs the expression of RA-induced CASP9. Serum-deprived MCF7 cells were treated for 45 min with 300-nM RA and specific siRNA targeting OGG1 or APE1; CASP9 expression levels were quantified by qPCR. To assess the transfection efficiency cells were co-transfected with pEGFP Vector (Clontech) and analyzed by FACS. (g, h) The recruitment of XPG and RPA to the CASP9 promoter and RARE. The statistical analysis derives from at least three experiments in triplicate (n ≥ 9; mean ± SD); *P < 0.01 (matched pairs t-test) compared to RA-unstimulated sample; **P < 0.01 (student t-test): comparison between SCR and specific siRNA; °°P < 0.01 (student t-test): comparison between the two amplicons.
