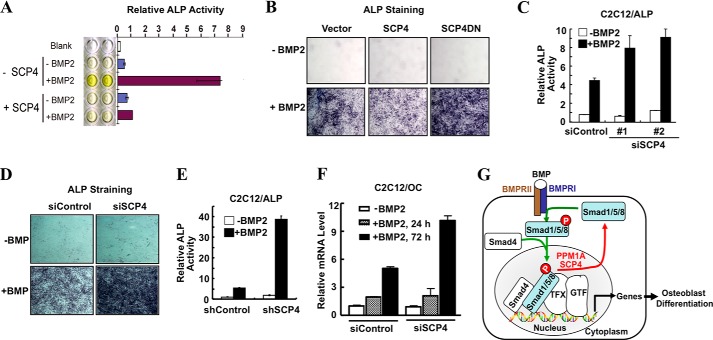
FIGURE 7.
SCP4 inhibits BMP-induced osteoblast-like differentiation. A, SCP4 inhibits BMP2-induced ALP activity in C2C12 cells. C2C12 cells were transfected with or without FLAG-SCP4 and treated with BMP2 (50 ng/ml) for 40 h. ALP activity was measured by absorbance at 405 nm after adding substrate pNPP. B, overexpression of SCP4 modulates BMP2-induced ALP expression. C2C12 cells stably expressing SCP4 or SCP4DN were cultured for 40 h with or without BMP2 (50 ng/ml) and then stained for ALP as described under “Experimental Procedures.” C, knockdown of SCP4 enhances BMP-induced ALP expression. C2C12 cells were transfected with siSCP4 or control siRNA. Cells were treated with BMP2 (50 ng/ml) for 40 h. ALP activity was measured by absorbance at 405 nm after adding substrate pNPP. D, knockdown of SCP4 accelerates BMP2-induced ALP expression. C2C12 cells were transfected with SCP4 siRNA or control siRNA. BMP2 (50 ng/ml) treatment and ALP staining were done as described for panel B. E, enhanced expression of ALP activity was assessed in stable knockdown cell line. F, enhanced expression of osteocalcin mRNA in SCP4 knockdown cells was assessed by qRT-PCR. G, a working model of SCP4 as a nuclear Smad phosphatase. SCP4 dephosphorylates Smad1/5/8, thereby turning off Smad-mediated transcriptional activation in the BMP signaling pathway. TFX and GTF represent Smad cofactors and general transcription factors, respectively. Error bars in panels C, E, and F indicate means ± S.E.