FIGURE 6.
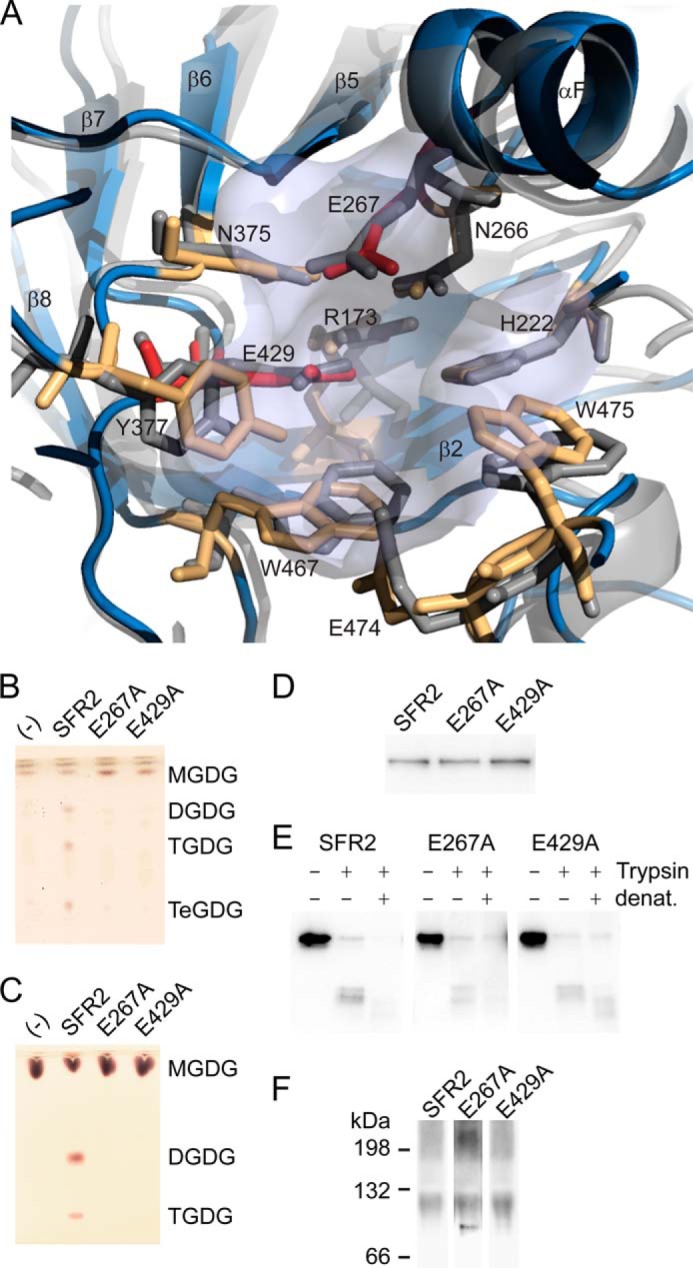
Glycosyl hydrolase catalytic residues are conserved in SFR2. A, ribbon representation of SFR2 model with catalytic site residues (light blue) shown compared with 1UWT (gray). Catalytic glutamates are shown in red, and residues known to contribute to catalytic chemistry or to sugar binding of glycosyl hydrolases appear in orange. B, thin layer chromatogram of lipids extracted from microsomes purified from yeast expressing MGDG synthase (MGD1) alone or MGD1 and SFR2 constructs. C, thin layer chromatogram of lipid extracts of glycosyl transfer assays under optimal conditions with MGDG (substrate) after 1 h. Chromatograms in B and C are stained for sugars and locations of substrate, and products (DGDG, TGDG, and TeGDG) are indicated. D, immunoblots of yeast microsomes expressing SFR2 or mutant constructs detected using a mixture of antisera recognizing the N or C terminus of SFR2. E, immunoblots of equivalent protein levels of yeast microsomes digested or mock-digested with trypsin (Trypsin) before or after denaturation (denat.) with heat and detergent as indicated at top. Detection was with antisera recognizing the C terminus of SFR2. F, immunoblots of yeast expressing SFR2 or mutant constructs separated by blue native-PAGE detected using a mixture of antisera recognizing the N or C terminus of SFR2.
