FIGURE 8.
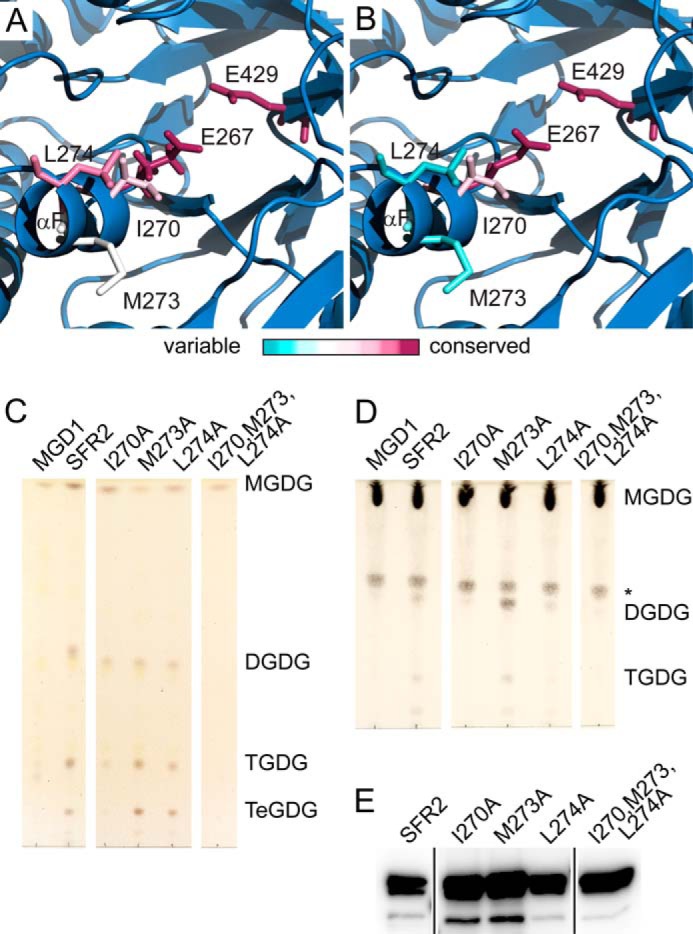
Hydrophobic residues are required for transferase activity. Representations of the SFR2 structure illustrating the side chains of active site glutamates and nearby hydrophobic patch. Side chains are colored by evolutionary conservation, as indicated by the ConSurf server for glycosyl hydrolase family 1 proteins that are SFR2-like (A) or excluding SFR2-like proteins (B). C, thin layer chromatogram of lipids extracted from microsomes purified from yeast expressing MGDG synthase (MGD1) alone or MGD1 and SFR2 constructs. White areas separate regions of the same TLC from which additional lanes were removed for clarity. D, thin layer chromatogram of lipid extracts of glycosyl transfer assays under optimal conditions with MGDG (substrate) after 1 h. White areas separate regions of the same TLC from which additional lanes were removed for clarity. An asterisk indicates a sugar-containing contaminant present in the substrate. Chromatograms in C and D are stained for sugars and locations of substrate and products (DGDG, TGDG, and TeGDG) are indicated. E, immunoblots of yeast microsomes used in B loaded with equal total protein and detected using a mixture of antisera specific to the N or C terminus of SFR2. Black lines separate regions of the same blot from which additional lanes were removed for clarity.
