FIGURE 3.
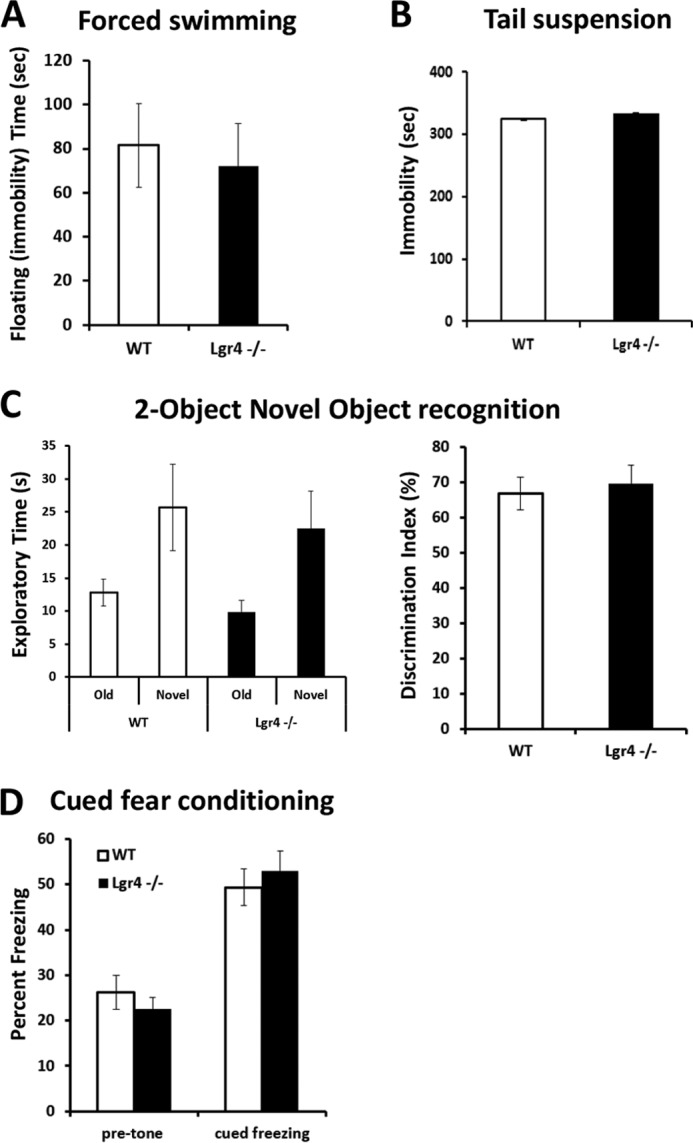
Lgr4−/− mice behave normally in despair and memory tests. A and B, forced swimming test (A) and tail suspension test (B) show a similar immobility time between Lgr4−/− mice (n = 10) and wild-type mice (n = 11). C, two-object novel object recognition test. Lgr4−/− and wild-type mice had a similar exploratory preference during training and retention sessions of the novel object recognition test (left); the discrimination index of Lgr4−/− mice (n = 10) also showed no difference compared with wild-type mice (n = 11, right). D, contextual fear-conditioning test showed no significant deficits between Lgr4−/− mice (n = 10) and wild-type mice (n = 11). Data are mean ± S.E.
