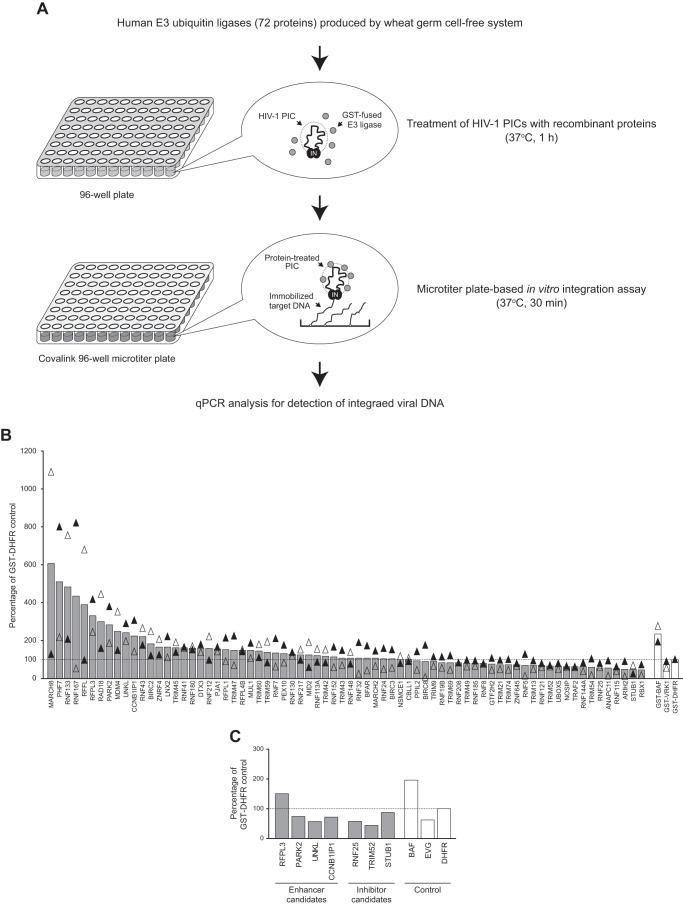
FIGURE 2.
Screening of human E3 ubiquitin ligases using the microtiter plate-based PIC assay. A, workflow of the screening assay. A library of human E3 ubiquitin ligases was generated by the wheat germ cell-free protein production system and further affinity purified using glutathione-Sepharose beads through a 96-well format filter unit. In total, 72 E3 ligases were incubated with PICs that had been isolated from VSV-G-pseudotyped HIV-1 vector-infected cells, and the reaction was subjected to the microtiter plate-based integration assay. The copy number of HIV-1 DNA integrated in immobilized target DNA was measured by qPCR analysis using HIV-1 LTR-specific primers. B, activity of HIV-1 PICs treated with E3 ubiquitin ligases (gray bars) and control proteins (GST-BAF (enhancer control), GST-VRK-1 (inhibitor control), and GST-DHFR (negative control), white bars) were analyzed by microtiter plate-based integration assay. Integrated viral DNA is shown as relative mean percentage over that of GST-DHFR-treated PICs (100%, dashed line) from two independent screening assays using different batches of proteins and HIV-1 PICs. Black and white triangles represent the first and second screening assay results, respectively. C, seven E3 ubiquitin ligases were selected as potential enhancers and inhibitors of HIV-1 PIC integration activity on the basis of the result of the first two rounds of screening assays and subjected to an additional microtiter plate-based integration assay together with control reactions (PICs treated with GST-BAF, 1 μm elvitegravir (EVG) and GST-DHFR). Integrated viral DNA detected is presented as a percentage of that of negative control protein (GST-DHFR, 100%, dashed line).