Figure 1.
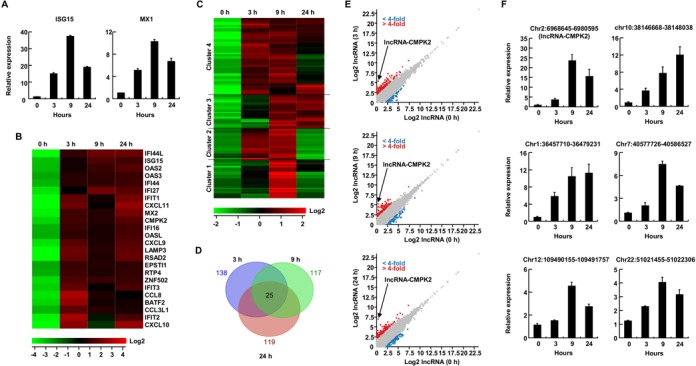
IFN-α induces hundreds of protein coding and long non-coding RNAs in human hepatocytes. (A) Induction of expression of ISG15 and Mx1 mRNAs at three time points following IFN-α addition in primary human hepatocytes measured by RT-qPCR. In this and the following panels, results are averages for at least two independent biological duplicate experiments with a minimum of two technical replicates per experiment. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. (B) Expression profiles of protein-coding RNAs that show over 10-fold change in expression following 3, 9 and 24 h of IFN-α treatment compared to untreated cells (samples shown as 0 h time point). The color scale is shown at the bottom. (C) Heat map and (D) Venn diagram of putative lncRNAs showing 4-fold or greater change in expression following IFN-α treatment. The time points shown are identical to those in panel (B). The color scale is shown at the bottom of heat map. (E) Scatter plots depicting the annotated putative lncRNAs that show a statistically significant change of 4-fold or more after 3 (top), 9 (middle) and 24 h (bottom) of IFN stimulation. The gray dots mark putative lncRNAs that did not show a significant change in expression. Red and blue dots correspond to upregulated and downregulated putative lncRNAs, respectively. The location of lncRNA-CMPK2 is shown. (F) RT-qPCR analysis of representative lncRNAs at indicated time points following IFN-α treatment. Strand-specific RT was performed using lncRNA-specific primers to ensure the specificity of detection, followed by qPCR. The locus of each analyzed lncRNA is shown on top. Numbers at the bottom refer to time point after IFN stimulation.
